When you think about the process of making paper, your mind might conjure images of massive vats of pulp, intricate machinery, and perhaps the final crisp sheet rolling off the line. But to be honest, there are many crucial components working tirelessly behind the scenes. Among these, the humble yet vital paper machine wire rolls often go unnoticed. These aren't just passive components; they are active participants in transforming a watery slurry of fibers into the paper we use every day. Frankly speaking, understanding their function is key to appreciating the sophistication of modern papermaking.
The Foundation: Understanding the Wire Section
The journey of paper begins on the wire section, often referred to as the Fourdrinier section. This is where the magic of dewatering and sheet formation truly takes place. The "wire" itself is a large, continuous loop of fine mesh fabric, moving at high speeds. It's supported by a complex arrangement of rolls, and it's these rolls that dictate the fabric's movement, tension, and stability. Without the precise engineering of these paper machine wire rolls, the formation of a uniform, strong paper web would be impossible.
The Role of the Forming Fabric
The forming fabric, or the "wire," is the heart of this section. It's a finely woven synthetic material designed to allow water to drain through while retaining the paper fibers. As the pulp slurry is pumped onto the moving fabric, gravity and vacuum systems work to pull water downwards. The rolls beneath and around the fabric guide its path, keep it taut, and ensure it runs smoothly without snagging or excessive wear.
Key Paper Machine Wire Rolls in the Fourdrinier Section
Within the Fourdrinier section, several types of rolls play distinct but interconnected roles:
- Breast Roll: This is the first roll the pulp slurry encounters. It's typically large in diameter and positioned at the "headbox" end of the machine. Its primary function is to distribute the stock evenly across the width of the forming fabric and to set the initial direction of the fabric's travel.
- Suction Couch Roll: Located further down the wire, this is a large, perforated roll with a vacuum inside. As the partially dewatered sheet passes over it, the vacuum aids in removing more water, consolidating the sheet and preparing it for the next stage.
- Table Rolls: These are a series of smaller diameter rolls that support the forming fabric in the initial dewatering zone. They are precisely spaced and aligned to provide a stable surface for the sheet to form on and to aid in drainage through the fabric.
- Felt Rolls: While technically part of the press section, some felt rolls are positioned to interact with the wire section to assist in initial sheet transfer and dewatering.
- Guide Rolls: These are smaller rolls used to maintain the correct tension and tracking of the forming fabric. They are often adjustable to make fine corrections to the fabric's path.
It's worth noting that the precision in manufacturing and alignment of these paper machine wire rolls is paramount. Even slight imperfections can lead to uneven sheet formation, fabric wear, and ultimately, reduced paper quality and increased operational costs.
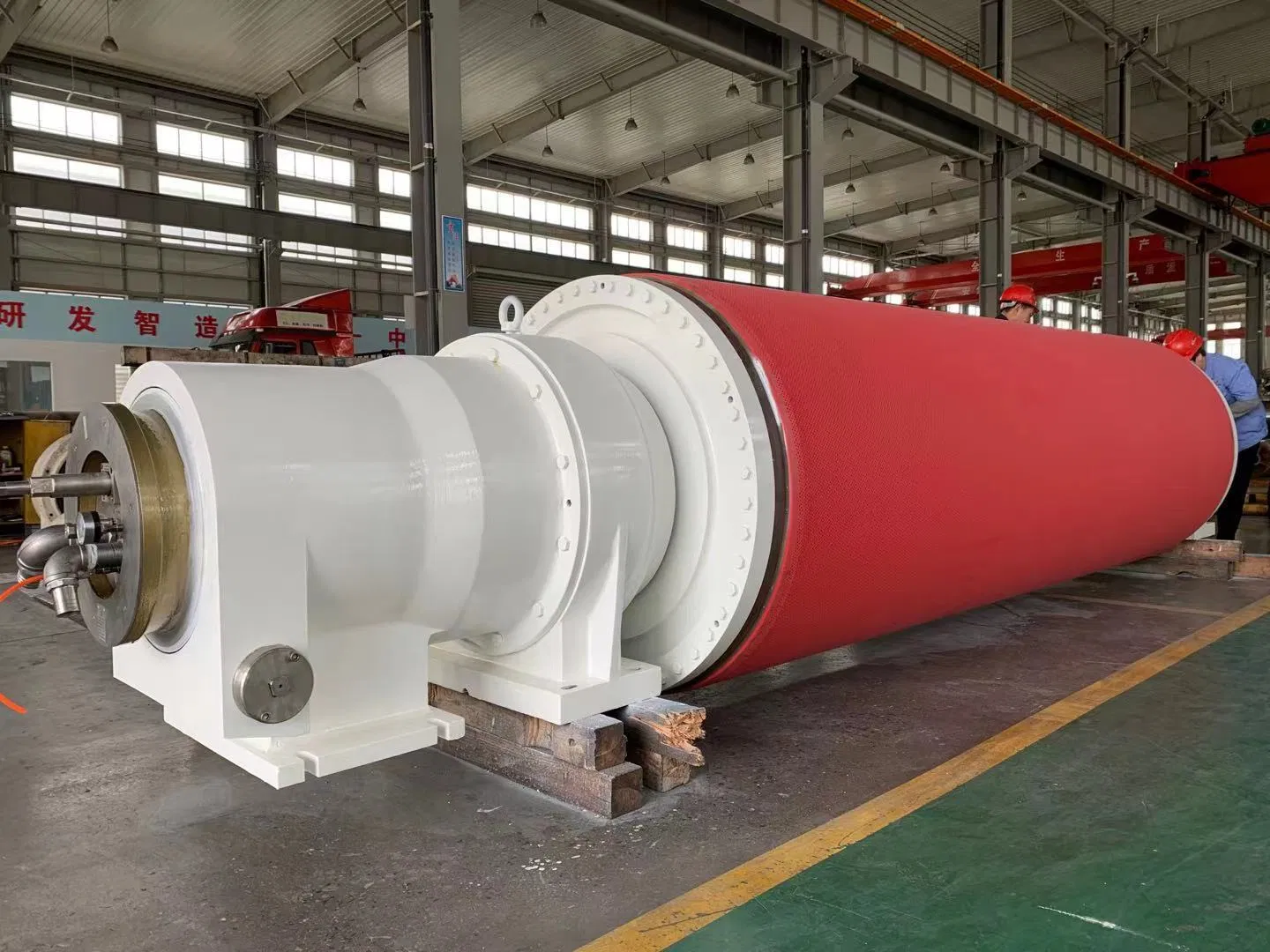

Beyond the Wire: Rolls in the Press and Dryer Sections
While the wire section is where sheet formation begins, paper machine wire rolls continue to be critical in subsequent sections. The press section, for instance, uses a series of rolls to squeeze out more water and compact the paper web, increasing its strength and density.
The Press Section's Role in Consolidation
In the press section, the damp paper web is passed between large, heavy rolls, often covered with felt. These rolls exert immense pressure, forcing out a significant amount of remaining water. The rolls here are designed for strength and smooth operation under high load. They help to:
- Further dewater the sheet.
- Increase the density and smoothness of the paper.
- Improve the paper's tensile strength.
- Reduce the energy required in the drying section.
Interestingly enough, the types of rolls used in the press section can vary depending on the paper grade being produced. Some might be granite rolls for a smooth finish, while others could be rubber-covered for specific pressure profiles.
The Dryer Section: Evaporating the Rest
The dryer section is where the bulk of the remaining water is evaporated. This section consists of a long series of large, steam-heated cylinders. The paper web passes over and under these cylinders, with additional rolls guiding its path. While these are primarily heated cylinders, they are still rolls within the larger paper machine system, and their smooth rotation and alignment are crucial for efficient drying and preventing web breaks. The tension maintained by the surrounding rolls is vital to ensure consistent contact with the heated surfaces.
Materials, Maintenance, and Longevity
The materials used in the construction of paper machine wire rolls are as important as their design. For the Fourdrinier section, rolls are often made from stainless steel or specialized composites to resist corrosion and wear from the constant contact with water and fibers. In the press and dryer sections, heavier materials like cast iron, steel, and granite are common, chosen for their strength and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
The Importance of Proper Maintenance
To be honest, the longevity and performance of paper machine wire rolls depend heavily on meticulous maintenance. Regular cleaning is essential to prevent the buildup of pulp, chemicals, or debris, which can cause uneven wear or damage to the forming fabric or felts. Lubrication of bearings is critical to ensure smooth rotation and prevent premature failure. Furthermore, periodic inspection for any signs of wear, pitting, or imbalance is vital. Many experts agree that a proactive maintenance schedule can significantly extend the life of these components and prevent costly downtime.
Have you ever wondered about the impact of a worn roll on the final product? A slightly out-of-round roll, for example, can create localized thin spots or thick spots in the paper web, leading to variations in strength, printability, and appearance. This is why precise alignment checks are a routine part of paper machine upkeep.
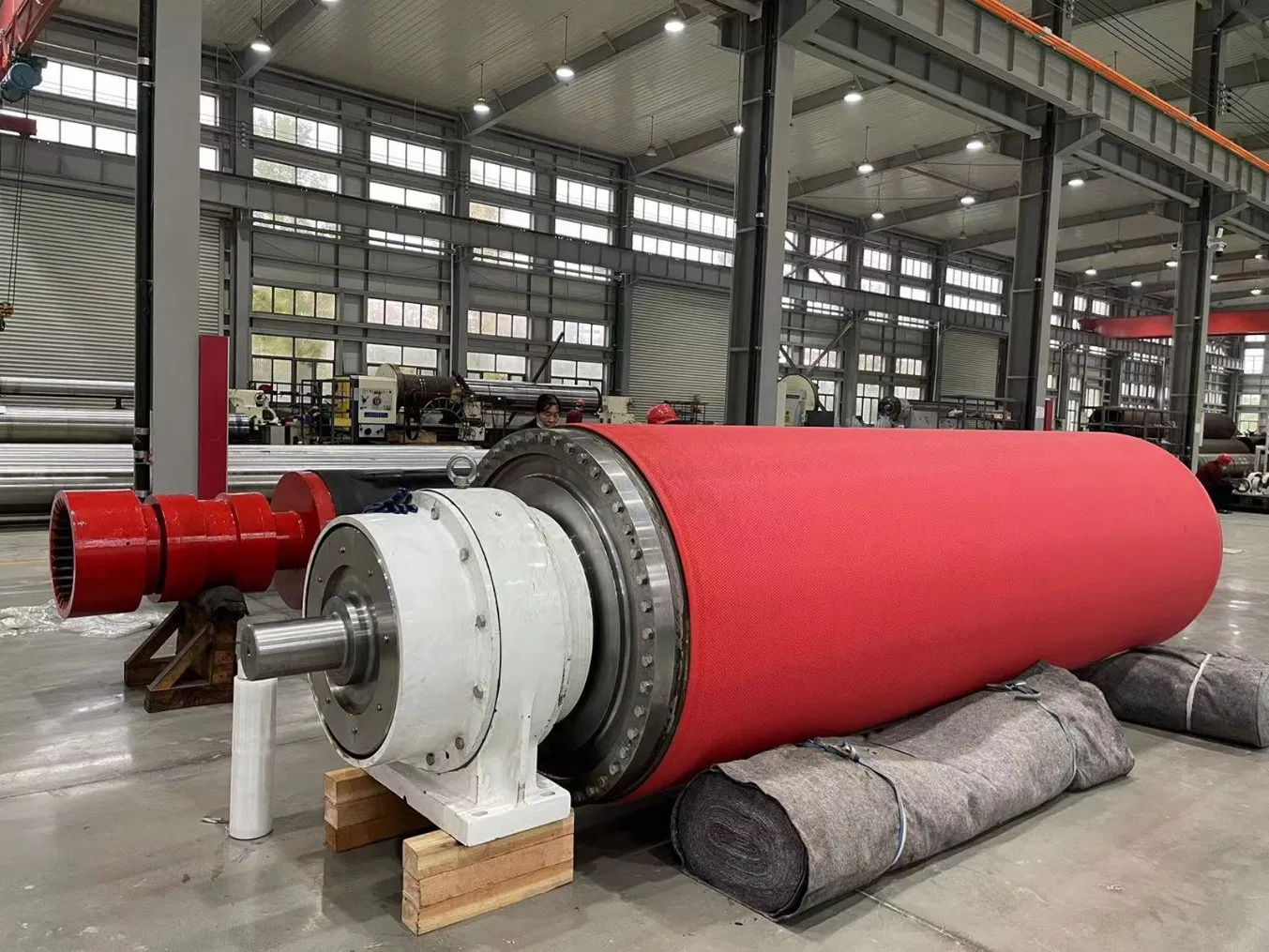

Innovations and Future Trends
The world of papermaking is constantly evolving, and this includes advancements in the design and materials of paper machine wire rolls. We're seeing a trend towards lighter, stronger materials that can withstand higher speeds and pressures. Advanced coatings are being developed to improve surface smoothness and reduce friction, leading to better energy efficiency and less wear.
Smart Rolls and Predictive Maintenance
Interestingly enough, the integration of sensors into these rolls is becoming more common. These "smart rolls" can monitor parameters like temperature, vibration, and rotational speed in real-time. This data can be used for predictive maintenance, alerting operators to potential issues before they lead to a breakdown. This shift from reactive to proactive maintenance is a significant step forward in optimizing paper machine performance.
The development of specialized rolls for different paper grades also continues. For instance, rolls designed for producing high-quality printing paper might have different surface finishes and material compositions compared to those used for packaging board. This customization ensures optimal performance for a wide range of paper products.
The Economic Impact of Efficient Rolls
Frankly speaking, the economic implications of well-functioning paper machine wire rolls are substantial. Efficient dewatering and pressing reduce the energy consumption in the dryer section, which is a major cost center in papermaking. Longer-lasting rolls mean less downtime for replacements and repairs, directly impacting production output. Furthermore, the consistent quality of paper produced thanks to precise roll performance contributes to customer satisfaction and market competitiveness.
In my experience, investing in high-quality paper machine wire rolls and adhering to a rigorous maintenance schedule is not an expense, but a strategic investment that pays dividends in terms of efficiency, product quality, and overall profitability. The seemingly simple act of a roll turning smoothly is the bedrock upon which a vast industry is built.
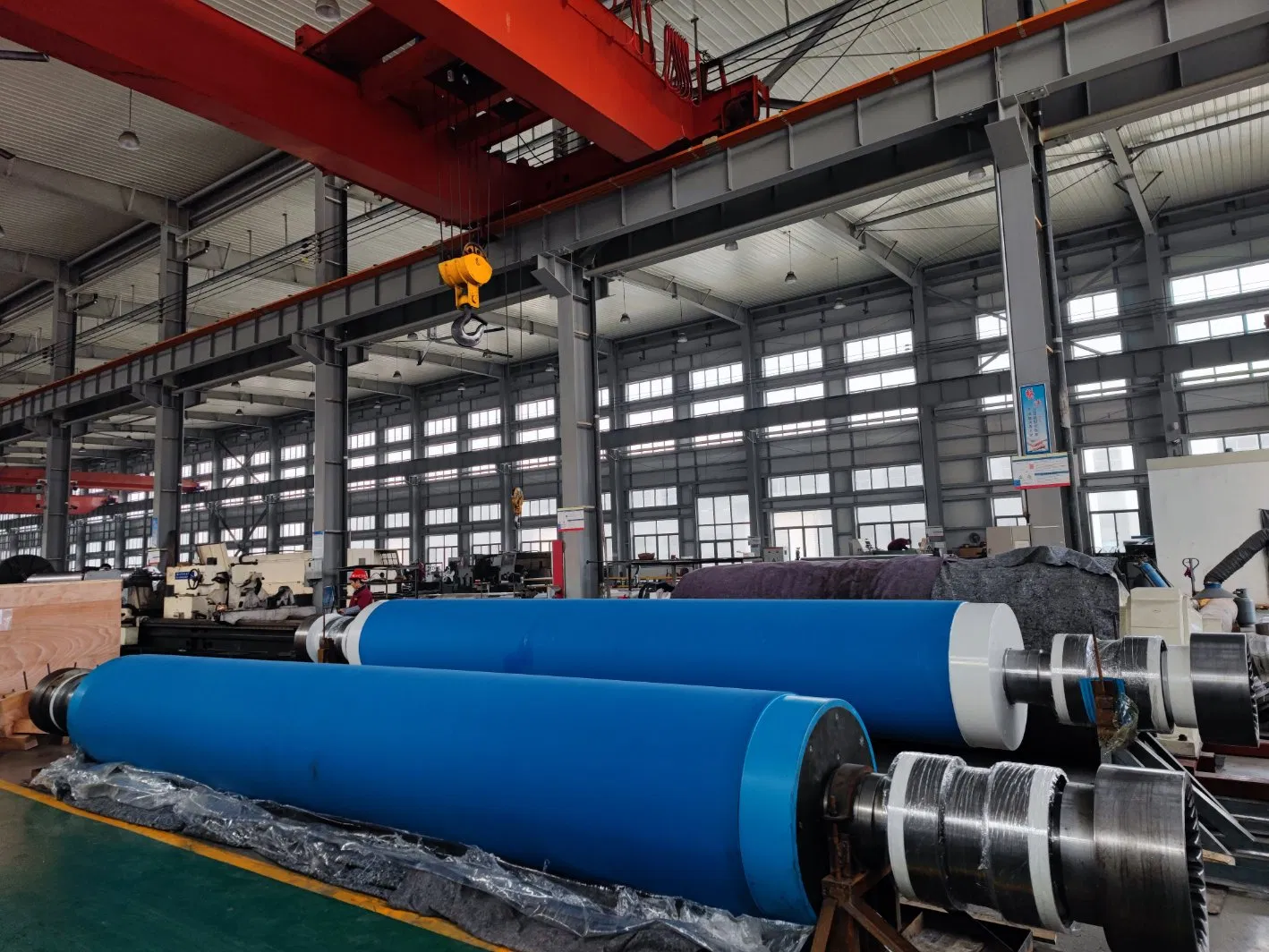

Understanding the intricate workings of paper machine wire rolls provides a deeper appreciation for the complex engineering that goes into producing the paper products we often take for granted. From the initial formation on the wire to the final consolidation in the press, these components are indispensable.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website:Paper machine wire rolls
About the author: A seasoned industry veteran with over two decades of experience in pulp and paper manufacturing, Alex Chen is a leading expert in papermaking machinery and process optimization. His insights are drawn from hands-on experience with various paper machine designs and a deep understanding of component performance, particularly paper machine wire rolls. Alex is passionate about sharing knowledge to improve efficiency and sustainability in the paper industry.