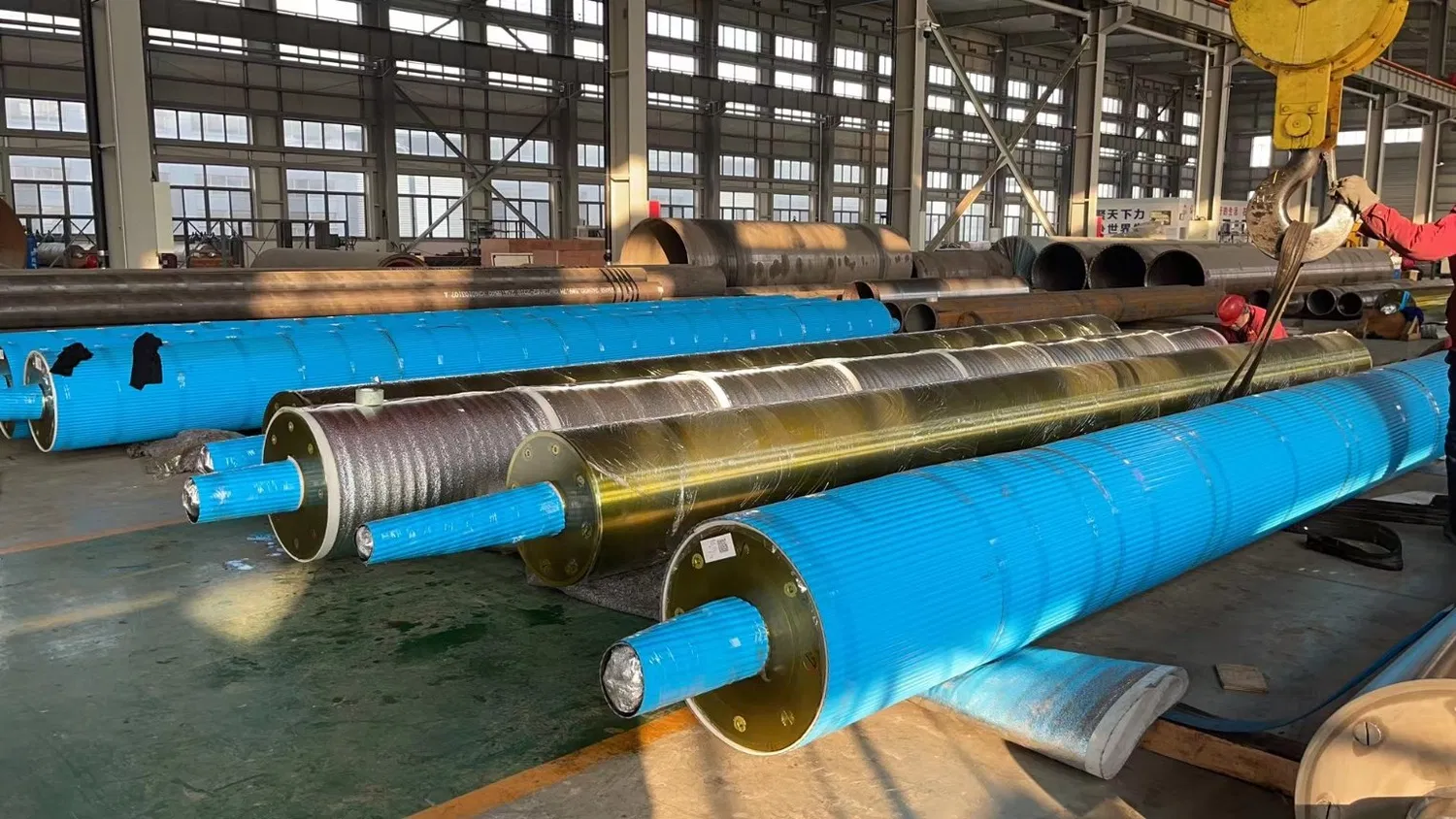
Paper, an ubiquitous material in our daily lives, from books and packaging to banknotes and tissues, owes its existence to a complex and fascinating manufacturing process. At the heart of this process lies the paper machine, a marvel of engineering with numerous intricate components working in perfect harmony. Among these crucial elements, paper-making rolls stand out as indispensable tools, each meticulously designed and manufactured to perform specific functions. Understanding the different types of paper-making rolls is key to appreciating the nuances of paper production and the remarkable technology behind it. These rolls are not merely cylindrical objects; they are sophisticated instruments that dictate the quality, texture, and final characteristics of the paper we use every day. Their design and material composition are carefully considered to withstand immense pressure, temperature variations, and continuous operation, ensuring a consistent and efficient paper-making process. Let's delve into the diverse world of these essential components and explore the fascinating roles they play.
The Press Section Rolls: Shaping and Dewatering
Within the paper machine, the press section plays a pivotal role in removing water from the paper web after it leaves the forming section and before it enters the dryer section. This section employs a series of press rolls, each type contributing uniquely to the dewatering and consolidation of the paper sheet. One prominent type is the suction press roll, characterized by its perforated shell and internal vacuum system. This design allows water to be drawn out of the paper web as it passes through the nip, significantly enhancing dewatering efficiency. Another important category is the grooved press roll, featuring grooves on its surface that provide channels for water to escape from the nip. These grooves can be designed in various patterns to optimize dewatering for different paper grades and machine conditions. Smooth press rolls, often made of materials like granite or specialized synthetic compounds, are used to impart smoothness and density to the paper surface. The strategic combination of these different press roll types in a press section is crucial for achieving the desired dryness content and surface properties of the paper before it proceeds to the energy-intensive drying stage. In essence, the press section rolls are the sculptors of the nascent paper web, molding its structure and removing excess water to prepare it for its final transformation.
Differentiating Press Roll Materials and Designs
The effectiveness of press rolls is not solely dependent on their type but also heavily influenced by the materials they are constructed from and their internal design. Traditionally, granite rolls were favored for their excellent nip uniformity and resistance to deflection under pressure. However, modern paper machines increasingly utilize composite rolls, which offer superior strength-to-weight ratios, enabling higher machine speeds and reduced energy consumption. These composite rolls often incorporate materials like carbon fiber or fiberglass in an epoxy matrix. Furthermore, the surface coverings of press rolls are critical. Rubber covers with varying hardness and groove patterns are commonly used, tailored to specific paper grades and dewatering requirements. Polyurethane covers offer enhanced durability and chemical resistance, making them suitable for demanding applications. The internal design of press rolls, particularly for suction rolls, involves complex engineering to optimize vacuum distribution and shell strength. Factors like shell thickness, perforation patterns, and internal baffling are carefully calculated to ensure efficient water removal and structural integrity under high operating loads. Choosing the right materials and design for press rolls is a complex balancing act, considering factors such as paper grade, machine speed, nip pressure, and desired paper properties.
Dryer Section Rolls: The Heat Masters
Following the press section, the dryer section is where the majority of the remaining water is removed from the paper web through evaporation. This section relies heavily on dryer cylinders, large, steam-heated rolls that are the workhorses of paper drying. Typically made of cast iron or steel, these cylinders are heated internally by steam, transferring heat to the paper web as it wraps around their surface. The surface finish of dryer cylinders is crucial for efficient heat transfer and preventing paper sticking. They are often chrome-plated or coated with other specialized materials to optimize these properties. Beyond the standard dryer cylinders, there are also felt rolls, which guide and support the dryer felts that carry the paper web through the dryer section. These rolls must be precisely aligned and balanced to ensure smooth felt operation and prevent wrinkles or breaks in the paper web. Guide rolls and tension rolls further contribute to the controlled movement and tension of both the paper web and the dryer felts within the dryer section. The dryer section is a significant energy consumer in the paper-making process, and the efficiency of the dryer rolls and the overall dryer configuration directly impact the energy footprint and production cost of paper manufacturing. Optimizing dryer roll design and operation is thus a continuous focus in the industry.
Forming Section Rolls: Initiating Paper Structure
The journey of paper begins in the forming section, where a dilute suspension of pulp fibers is transformed into a nascent paper web. This critical stage utilizes various types of rolls to facilitate fiber orientation and initial drainage. The breast roll is the first roll the pulp slurry encounters as it is ejected from the headbox onto the forming fabric. It plays a crucial role in controlling the initial formation of the paper web and ensuring even fiber distribution. Forming boards and foils, though not rolls in the traditional sense, are often considered part of the forming roll system. They are stationary elements positioned beneath the forming fabric to create pulses and pressure variations that aid in water removal and fiber orientation. Table rolls, rotating beneath the forming fabric, also contribute to drainage and web formation. These rolls, in conjunction with the forming fabric, work to gently remove water while encouraging fibers to interlock and create a uniform sheet structure. The forming section is arguably the most delicate part of the paper machine, as it sets the foundation for the paper's final properties. The precise design and operation of the forming rolls and related elements are paramount for achieving consistent paper quality and minimizing defects right from the outset of the paper-making process. Have you ever wondered why different papers have varying textures? Much of that difference can be traced back to the forming section and how these initial rolls shape the very structure of the paper.
Calender Rolls: Fine-Tuning Paper Surface Properties
As the paper web exits the dryer section, it often passes through a calender section, a series of rolls designed to refine the paper's surface properties, such as smoothness, gloss, and thickness uniformity. Calender stacks are composed of multiple rolls arranged in a vertical configuration, creating nips through which the paper passes under pressure. Hard nip calenders utilize rolls with hard surfaces, such as steel or chilled iron, to impart a smooth and glossy finish. Soft nip calenders, on the other hand, employ rolls with softer covers, like polymer or composite materials, to achieve a smoother surface without excessive gloss, often preferred for printing grades. Controlled crown rolls, also known as variable crown rolls, are sophisticated calender rolls that can adjust their profile to compensate for roll deflection and nip pressure variations across the paper web width. This allows for precise control over the calendering process and ensures uniform paper properties across the entire sheet. Calendering is a crucial step for achieving the desired printability and aesthetic qualities of many paper grades, especially those used for magazines, brochures, and high-quality packaging. The selection and configuration of calender rolls are carefully tailored to the specific paper grade and target surface characteristics.
Guide Rolls and Tension Rolls: Ensuring Smooth Operation
Beyond the rolls directly involved in forming, pressing, drying, and calendering, a multitude of guide rolls and tension rolls are essential for the smooth and efficient operation of the entire paper machine. Guide rolls, as their name suggests, are used to direct the paper web and the various machine fabrics (forming fabric, press felts, dryer felts) through their respective paths within the machine. They are strategically placed to ensure proper web tracking, prevent wrinkles, and maintain consistent tension. Tension rolls are specifically designed to control and maintain the tension of the paper web and machine fabrics. Precise tension control is vital for preventing web breaks, ensuring uniform dewatering and drying, and achieving consistent paper quality. These rolls can be equipped with sophisticated tension control systems that automatically adjust roll speed or nip pressure to maintain the desired tension levels. While guide rolls and tension rolls may not directly transform the paper web's properties in the same way as press or dryer rolls, their contribution to the overall stability and efficiency of the paper machine is undeniable. They are the unsung heroes, working tirelessly behind the scenes to keep the entire complex system running smoothly.
Material Considerations in Paper-Making Rolls: Durability and Performance
The materials used in the construction of paper-making rolls are critical to their performance, longevity, and overall efficiency. As mentioned earlier, cast iron and steel are traditional materials for dryer cylinders and calender rolls due to their heat conductivity and strength. However, advancements in materials science have led to the increasing adoption of composite materials, particularly for press rolls and some dryer rolls. Composites offer advantages like reduced weight, higher strength-to-weight ratios, and improved vibration damping, which can lead to energy savings and increased machine speeds. Roll covers are another crucial aspect of material selection. Rubber covers, available in a wide range of hardness and chemical resistance, are widely used for press rolls and some calender rolls. Polyurethane covers provide enhanced durability and abrasion resistance, while specialized coatings like ceramics and carbides can be applied to rolls for specific applications requiring extreme wear resistance or surface properties. The choice of materials must consider factors such as the specific roll function, operating conditions (temperature, pressure, chemical exposure), paper grade being produced, and desired roll lifespan. Material selection is a complex engineering decision that directly impacts the performance, maintenance requirements, and overall cost-effectiveness of paper-making rolls.
Advances and Innovations in Paper-Making Roll Technology
The field of paper-making roll technology is continuously evolving, driven by the industry's ongoing pursuit of improved efficiency, paper quality, and sustainability. One significant area of innovation is in roll cover technology. Researchers and engineers are constantly developing new cover materials with enhanced dewatering capabilities, wear resistance, and reduced energy consumption. Smart rolls, equipped with sensors and actuators, are emerging as a promising technology. These rolls can monitor and adjust parameters like nip pressure, temperature, and vibration in real-time, optimizing the paper-making process dynamically. Energy-efficient roll designs are also gaining traction, focusing on reducing roll weight, minimizing friction, and improving heat transfer efficiency in dryer rolls. Furthermore, advancements in manufacturing techniques, such as precision machining and advanced composite fabrication, are enabling the production of rolls with tighter tolerances and improved performance characteristics. These innovations are not just incremental improvements; they represent a continuous drive to push the boundaries of paper-making technology, making the process more efficient, sustainable, and capable of producing ever-higher quality paper products. It's an exciting area where engineering ingenuity directly translates to tangible improvements in a fundamental industry.
Conclusion: The Indispensable Role of Paper-Making Rolls
As we've explored, understanding the different types of paper-making rolls is fundamental to grasping the intricacies of paper manufacturing. From the forming section where the initial web structure is created, through the press and dryer sections where water is meticulously removed, to the calender section where surface properties are refined, each type of roll plays a vital and precisely defined role. The selection of materials, the intricacies of roll design, and the ongoing innovations in roll technology all underscore the critical importance of these components in producing the vast array of paper products we rely on daily. Paper-making rolls are not simply passive components; they are active participants in shaping the very nature of paper, influencing its strength, texture, printability, and countless other characteristics. Their continuous evolution reflects the paper industry's commitment to efficiency, quality, and sustainability. By understanding the diverse world of paper-making rolls, we gain a deeper appreciation for the engineering marvel that is the modern paper machine and the remarkable journey from pulp to paper.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website: Paper-making rolls