The heart of any paper machine lies in its intricate system of rolls, each performing a critical function in transforming pulp into the paper we use every day. From dewatering and pressing to calendering and reeling, the materials used in these rolls directly impact efficiency, product quality, and operational costs. Frankly speaking, a thorough paper machine roll material comparison is not just an academic exercise; it's a fundamental aspect of optimizing paper production. In my experience, selecting the wrong material can lead to premature wear, increased downtime, and subpar paper characteristics.
Have you ever wondered what makes a paper machine roll last longer or perform better? It often comes down to the sophisticated materials engineered for each specific role. This article delves into a comprehensive paper machine roll material comparison, examining the common materials used for various roll types and the factors that influence their selection.
Understanding the Crucial Roles of Paper Machine Rolls
Before we dive into the materials themselves, it's essential to understand the diverse functions these rolls perform. Each section of the paper machine presents unique challenges, demanding specific material properties.
The Forming Section
In the initial stages, the forming section uses rolls like the breast roll and table rolls. Their primary role is to support the forming fabric and facilitate initial drainage. While less demanding than other sections, their surface smoothness and resistance to abrasion are still important.
The Press Section
This is where significant dewatering occurs. Press rolls, often covered with resilient materials, apply pressure to squeeze out water. The materials here must withstand immense pressure, resist crushing, and provide a uniform nip to ensure consistent sheet density and thickness. This section is a prime candidate for detailed paper roll selection considerations.
The Dryer Section
Dryer rolls are heated to evaporate remaining moisture from the paper web. Their primary requirement is excellent heat transfer and a smooth surface to prevent sticking and marking.
The Calender and Reel Sections
Calender rolls are used to smooth and impart gloss to the paper surface. They require materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures without deforming. Reel rolls are responsible for winding the finished paper into large rolls, demanding precision and durability.
A Deep Dive into Press Roll Covering Materials
The press section is arguably where the most critical material choices are made for rolls. The coverings on press rolls are designed to absorb water, provide a uniform pressing force, and protect the paper web.
Rubber Coverings
Rubber remains a workhorse in the paper industry due to its versatility and cost-effectiveness. Different types of rubber are used, each with specific properties:
- Natural Rubber: Offers excellent elasticity and resilience, making it good for shock absorption and providing a soft nip. However, it can be susceptible to degradation from chemicals and heat.
- Synthetic Rubbers (e.g., SBR, EPDM, Nitrile): These offer a wider range of properties. SBR (Styrene-Butadiene Rubber) provides good abrasion resistance. EPDM (Ethylene Propylene Diene Monomer) excels in heat and chemical resistance. Nitrile rubber is known for its oil and grease resistance. The specific formulation is key to achieving the desired performance.
- Polyurethane: Increasingly popular, polyurethane coverings offer exceptional abrasion resistance, high load-bearing capacity, and excellent resistance to chemicals and hydrolysis. They can be formulated to provide a very precise and uniform nip, leading to improved sheet properties.
When considering a paper machine roll material comparison for the press section, the choice between rubber and polyurethane often comes down to a balance of cost, desired nip uniformity, and resistance to specific operating conditions.
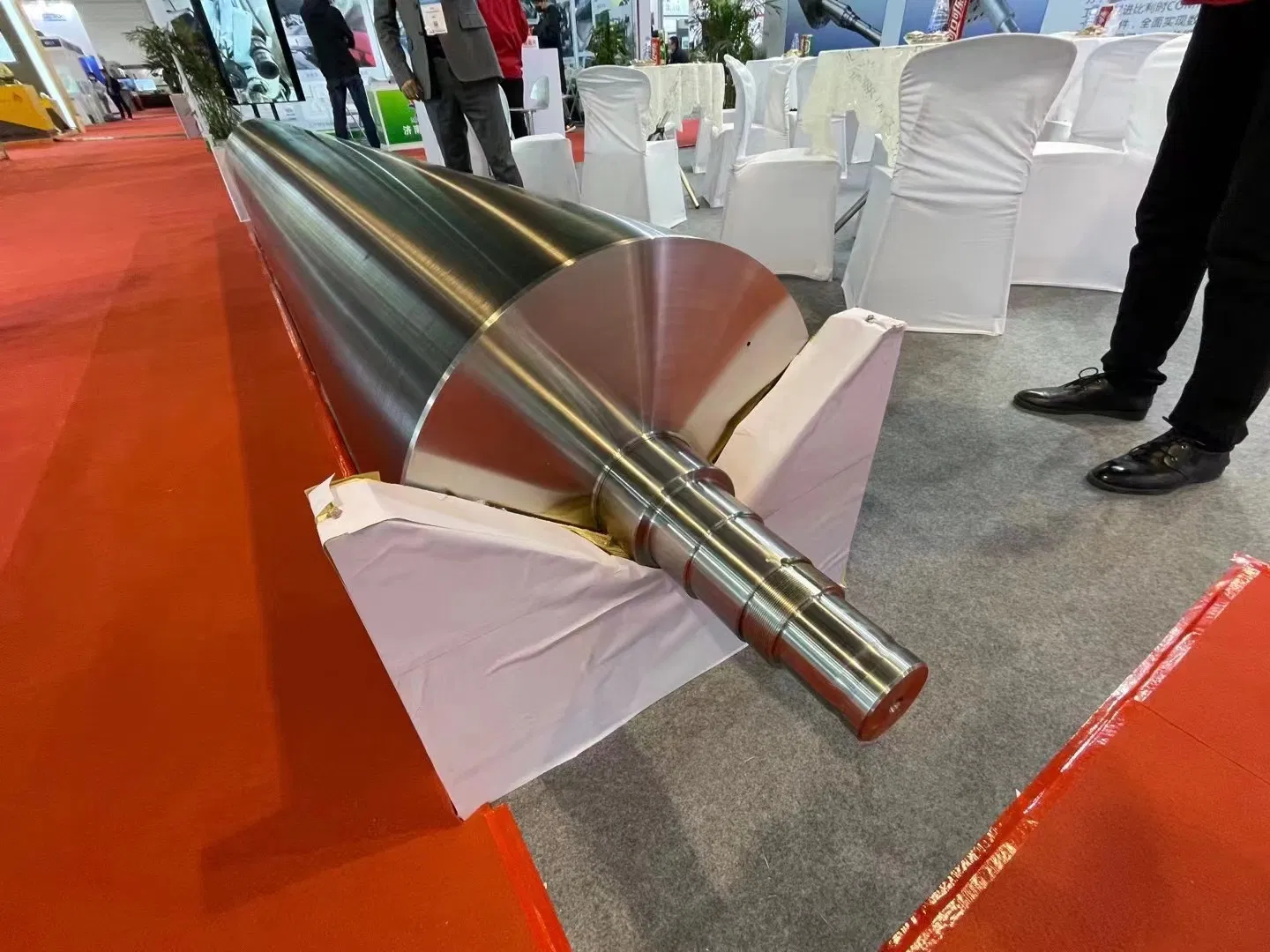

Felt Materials in the Press Section
While not roll coverings themselves, the press felts work in conjunction with the press rolls. The materials used in felts – typically synthetic fibers like polyester, polyamide, and polypropylene – are crucial for efficient water removal and preventing marking. The interaction between the felt and the roll surface is a vital part of the overall dewatering process.
Suction Roll Shell Materials: Balancing Strength and Porosity
Suction rolls are integral to dewatering, utilizing vacuum to pull water through the forming fabric or felt. The shell of a suction roll must be strong enough to withstand the vacuum pressure while also being porous enough to allow water passage.
Stainless Steel
This is a common and reliable choice. Various grades of stainless steel are used, offering excellent corrosion resistance, which is vital in the wet end of the paper machine. Its strength ensures the structural integrity of the roll under vacuum.
Bronze and Brass Alloys
Historically, bronze and brass were widely used. They offer good machinability and corrosion resistance. However, they are generally not as strong as stainless steel and can be more susceptible to wear in certain applications.
Composite Materials
In some advanced applications, composite materials are being explored. These can offer a combination of strength, light weight, and tailored porosity. However, their cost and long-term durability in the harsh paper mill environment are still under evaluation for many paper machine roll material comparison studies.
The drilling pattern of the suction roll shell is also a critical design element, influencing drainage efficiency and the risk of plugging. This, in turn, affects the choice of shell material and its ability to withstand the forces involved.
Materials for Calender and Dryer Rolls
These sections have different demands compared to the press section.
Calender Rolls
Calender rolls often require materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures to achieve a smooth, glossy finish.
- Chilled Iron: A traditional and robust material, chilled iron offers excellent hardness and wear resistance, making it suitable for high-pressure calendering.
- Steel: Various steel alloys can be used, often with specialized coatings or surface treatments to enhance their performance.
- Composite Rolls (e.g., Bosson Rolls): These modern rolls often consist of a steel core with a specialized composite or polymer outer shell. They offer excellent temperature control and a uniform nip, leading to superior paper finishing.
Dryer Rolls
Dryer rolls primarily need to be excellent heat conductors and maintain a smooth surface.
- Cast Iron: The most common material for dryer cans due to its excellent heat transfer properties and durability.
- Steel: Some specialized dryer sections might use steel, particularly for high-pressure applications or specific drying technologies.
It's worth noting that the surface finish and coatings applied to these rolls are as important as the base material for achieving the desired paper quality.
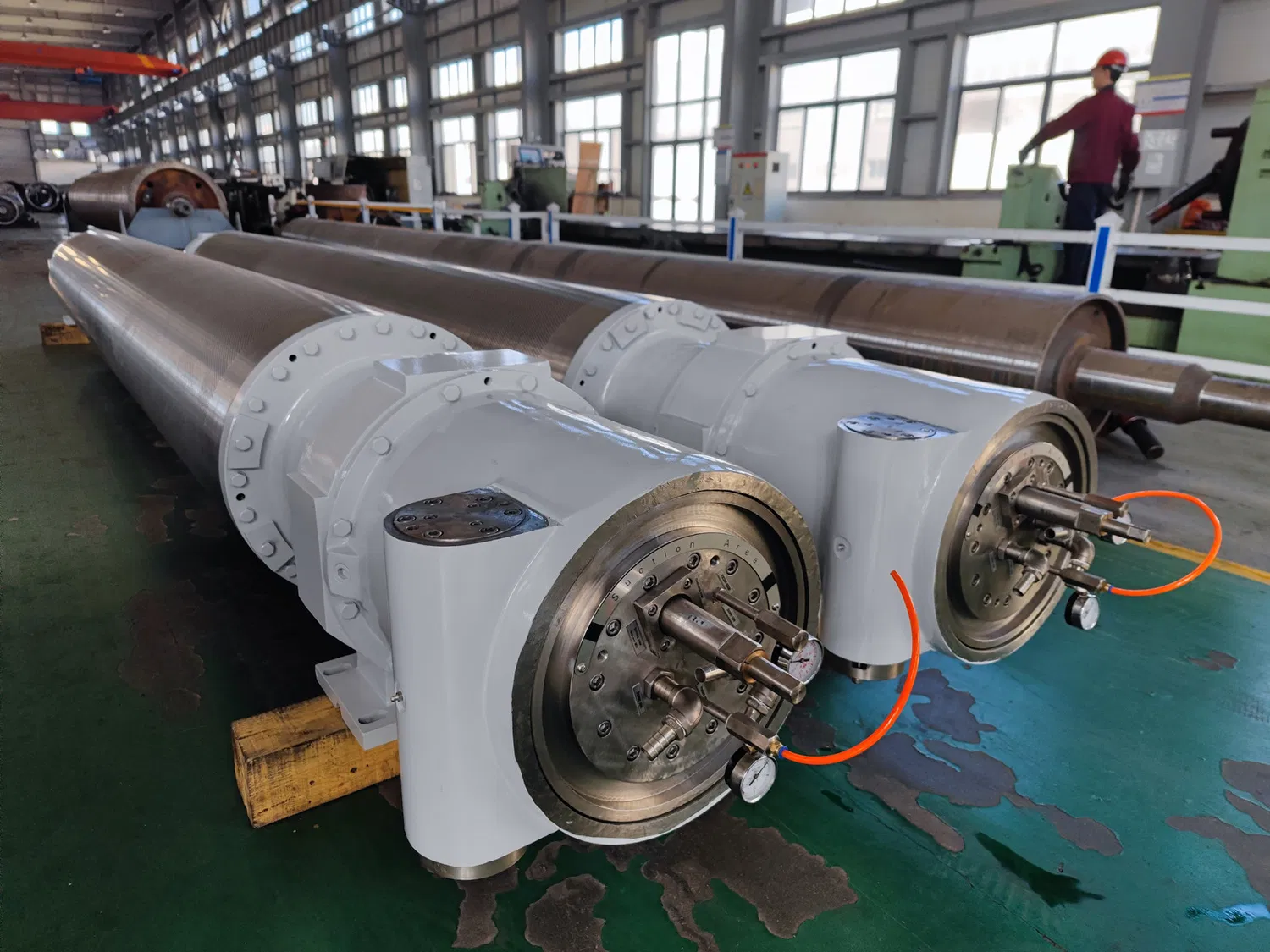

Factors Influencing Paper Machine Roll Material Selection
When conducting a paper machine roll material comparison for your specific operation, several key factors must be considered:
- Type of Paper Being Produced: Different paper grades (e.g., tissue, printing paper, packaging board) have varying requirements for surface finish, strength, and moisture content, which dictate the necessary roll properties.
- Operating Conditions: This includes temperature, pressure, chemical exposure (e.g., sizing agents, bleaching chemicals), and the presence of abrasive particles in the pulp slurry.
- Desired Paper Quality: Factors like smoothness, gloss, caliper uniformity, and printability are directly influenced by the rolls.
- Machine Speed and Efficiency: Higher speeds often demand more durable and precisely engineered roll materials to maintain consistent performance and minimize downtime.
- Maintenance and Lifespan: The cost of maintenance, expected lifespan of the roll covering, and ease of replacement are crucial economic considerations.
- Cost: While performance is paramount, the initial investment and ongoing operational costs associated with different materials must be balanced.
Interestingly enough, advancements in material science are constantly introducing new options. For instance, ceramic coatings are being explored for their extreme hardness and wear resistance in specific applications.
The Importance of a Comprehensive Paper Machine Roll Material Comparison
To reiterate, a detailed paper machine roll material comparison is not a one-time task. As technology evolves and production demands change, reassessing the materials used for your paper machine rolls is essential. Investing in the right materials can lead to:
- Improved Paper Quality: Uniform pressing, better surface finish, and consistent caliper.
- Increased Machine Efficiency: Reduced downtime due to fewer roll failures or wear-related issues.
- Lower Operational Costs: Longer roll life, reduced energy consumption, and fewer unscheduled maintenance interventions.
- Enhanced Safety: Reliable components reduce the risk of unexpected failures.
Frankly speaking, the performance of your paper machine is intrinsically linked to the quality and suitability of its constituent parts, and the rolls are no exception. By understanding the properties and applications of various paper machine roll materials, you can make informed decisions that drive profitability and product excellence.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website:paper machine roll materials
About the author: A seasoned paper manufacturing consultant with over 15 years of hands-on experience, Sarah Chen specializes in optimizing paper machine efficiency and product quality. Her expertise spans material science, process engineering, and troubleshooting complex operational challenges within the pulp and paper industry. Sarah is passionate about sharing practical insights to help manufacturers achieve peak performance.