The paper industry is a fascinating blend of tradition and cutting-edge technology. At the heart of this complex machinery are the rolls, and the surfaces of these rolls are critical to the quality and efficiency of paper production. Frankly speaking, the choice of paper machine roll coatings can make or break your operation. It's not just about preventing wear and tear; it's about optimizing everything from sheet formation to energy consumption. This comprehensive guide to selecting paper machine roll coatings aims to demystify the process, offering insights that can lead to significant improvements in your paper manufacturing.
The Crucial Role of Roll Coatings in Paper Machines
Paper machines are massive, intricate systems where paper is formed, pressed, dried, and finished. Each section of the machine employs various types of rolls, and their surfaces interact directly with the paper web. These interactions demand specific properties from the roll coatings. To be honest, without the right coating, you're looking at potential issues like sticking, abrasion, uneven pressing, poor heat transfer, and ultimately, reduced paper quality and increased downtime.
Consider the press section, for instance. Here, rolls are responsible for squeezing water out of the paper web. The coating needs to be smooth enough to prevent marking the paper, yet durable enough to withstand the immense pressure and the presence of water and chemicals. In the drying section, rolls are heated, and the coating must facilitate efficient heat transfer while preventing the paper from sticking to the hot surface. This highlights the diverse demands placed upon these seemingly simple components.
Understanding Different Types of Paper Machine Rolls and Their Coating Needs
Different sections of a paper machine have unique requirements for their rolls, and consequently, their coatings. Let's break down some key areas:
- Forming Section: Rolls here, like suction rolls and couch rolls, need coatings that offer good drainage, wear resistance, and prevent stock buildup.
- Press Section: This is where pressure is applied to remove water. Rolls like suction press rolls, plain press rolls, and breaker stacks require coatings that are smooth, non-marking, water-repellent, and highly durable to withstand significant nip forces.
- Dryer Section: Heated dryer cans require coatings that ensure excellent heat transfer and prevent the paper web from sticking.
- Calender Section: Rolls in the calender stack are used to smooth and polish the paper. Coatings here must provide a very smooth, non-abrasive surface to achieve the desired gloss and smoothness without damaging the paper.
- Coating Section: If your machine has a coating application section, the rolls involved (e.g., applicator rolls, metering rods) need specialized coatings for precise and even application of coating materials.
Interestingly enough, the type of paper being produced also plays a significant role. Newsprint has different requirements than fine paper or packaging board. This interplay between machine section and paper type is fundamental to making the right selection.
Key Factors in Selecting the Right Paper Machine Roll Coating
Choosing the optimal paper machine roll coating isn't a one-size-fits-all decision. It requires a careful evaluation of several critical factors. My experience has shown that neglecting even one of these can lead to suboptimal performance.
1. Material Properties and Performance Requirements
This is perhaps the most crucial aspect. You need to consider:
- Hardness: A harder coating generally offers better wear resistance but can be more prone to chipping or cracking under impact.
- Toughness: This refers to the coating's ability to resist fracture and impact damage. A tough coating can withstand the rigors of the paper machine environment.
- Adhesion: The coating must adhere strongly to the base roll material to prevent delamination, which can cause catastrophic failures.
- Chemical Resistance: Paper manufacturing involves various chemicals, water, and pulp. The coating must resist degradation from these substances.
- Temperature Resistance: Particularly important for dryer section rolls, the coating must withstand high operating temperatures without losing its integrity or performance.
- Surface Finish: The required smoothness or texture of the coating is vital for preventing paper marking, ensuring good release, or facilitating specific finishing properties.
For example, a press roll might benefit from a robust, slightly yielding coating that offers good grip and water removal, while a dryer roll needs a slick, heat-conductive surface.
2. Environmental Conditions and Operational Demands
The specific environment within your paper mill and the operational demands placed on the rolls are paramount.
- Operating Speed: Higher speeds can increase friction and heat, requiring coatings that can handle these conditions.
- Nip Loads: The pressure applied in the press section directly impacts the stress on the roll coating.
- Web Material: The type of paper being produced (e.g., coated vs. uncoated, abrasive fillers) will influence the wear rate on the coating.
- Moisture and Chemical Exposure: As mentioned, the presence of water, sizing agents, fillers, and other chemicals can degrade certain coatings.
- Cleaning Regimes: How the rolls are cleaned can also affect coating longevity. Some coatings are more susceptible to damage from aggressive cleaning agents or methods.
It's worth noting that even seemingly minor variations in these conditions can necessitate a different coating solution.
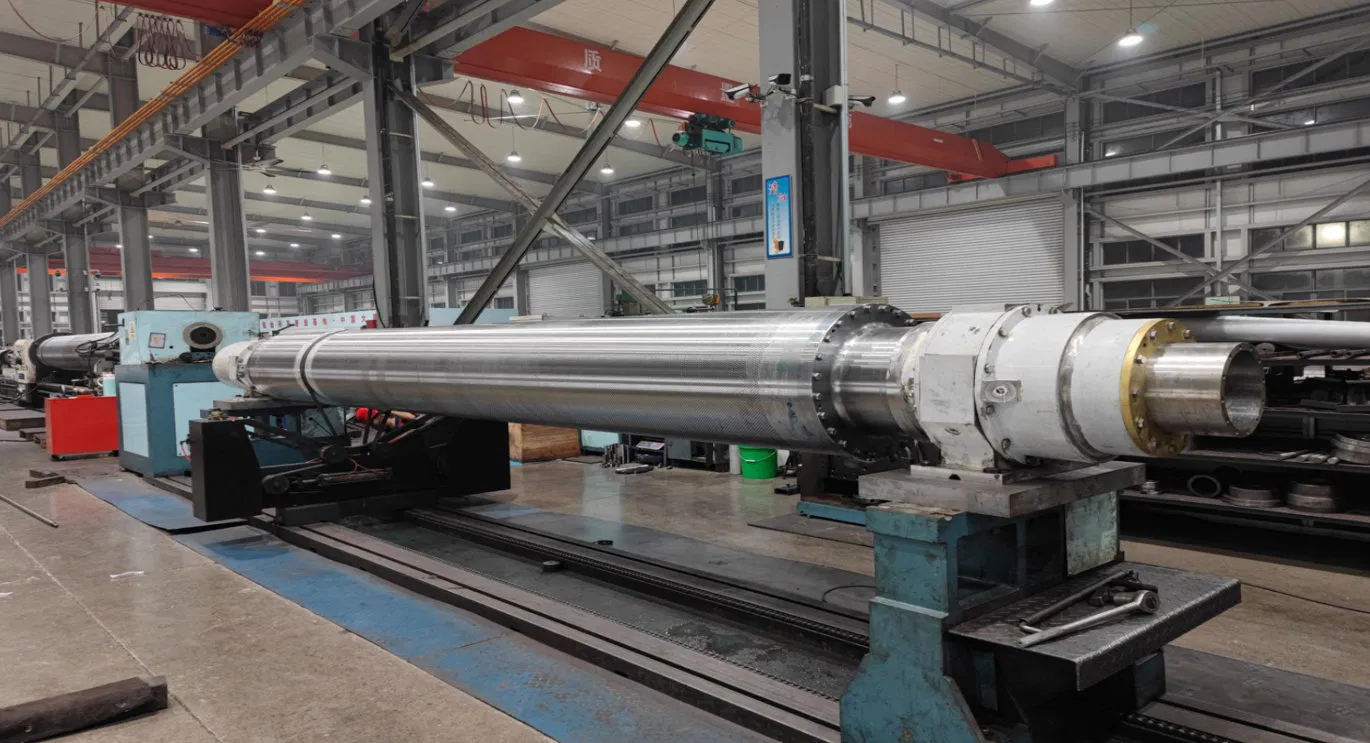

3. Cost-Effectiveness and Lifecycle Value
While initial cost is a factor, it's essential to consider the long-term value. A cheaper coating that fails prematurely will incur higher costs due to:
- Downtime: Lost production time is incredibly expensive.
- Maintenance and Replacement: Frequent recoating or roll replacement adds up.
- Paper Quality Issues: Off-spec paper leads to waste, reprocessing, or customer complaints.
Therefore, a slightly more expensive, high-performance coating that lasts longer and prevents issues can be far more cost-effective in the long run. This is a key aspect of a smart guide to selecting paper machine roll coatings.
Common Types of Paper Machine Roll Coatings Explained
The world of roll coatings is diverse, with various materials offering unique benefits. Understanding these common types is crucial for informed decision-making.
1. Elastomeric Coatings (Rubber and Polyurethane)
Elastomeric coatings are perhaps the most widely used in paper machines, especially in the press section.
- Rubber: Natural and synthetic rubbers offer good resilience, shock absorption, and water-repellent properties. Different compounds can be formulated to achieve specific hardness and wear characteristics. They are excellent for applications requiring good grip and dewatering.
- Polyurethane: Polyurethanes are known for their exceptional abrasion resistance, toughness, and chemical resistance. They can be formulated to be very hard or relatively soft, offering a wide range of performance capabilities. Polyurethane coatings are often chosen for their durability and ability to maintain their properties under demanding conditions.
In my experience, the precise formulation of these elastomers is where the magic happens, allowing for tailored performance for specific nip conditions and paper types.
2. Polymer Coatings (PTFE, PEEK, etc.)
These advanced polymer coatings offer specialized properties, often for high-performance applications.
- PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): Famous for its non-stick properties and low coefficient of friction, PTFE coatings are excellent for preventing paper buildup and ensuring smooth release, especially in dryer sections or on certain calender rolls.
- PEEK (Polyetheretherketone): PEEK is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its exceptional mechanical strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance. It's used in highly demanding applications where extreme conditions are encountered.
These advanced materials can be more expensive but offer unparalleled performance where traditional materials fall short.
3. Ceramic Coatings
Ceramic coatings, often applied through thermal spray processes, provide extremely hard and wear-resistant surfaces.
- Benefits: They offer superior resistance to abrasion, corrosion, and high temperatures. They are particularly useful in harsh environments or where extreme wear is a concern.
- Considerations: They can be brittle, so toughness is a critical factor in their formulation and application. Surface finish can also be a consideration for paper contact.
Many experts agree that ceramic coatings are becoming increasingly important for specialized applications requiring ultimate durability.
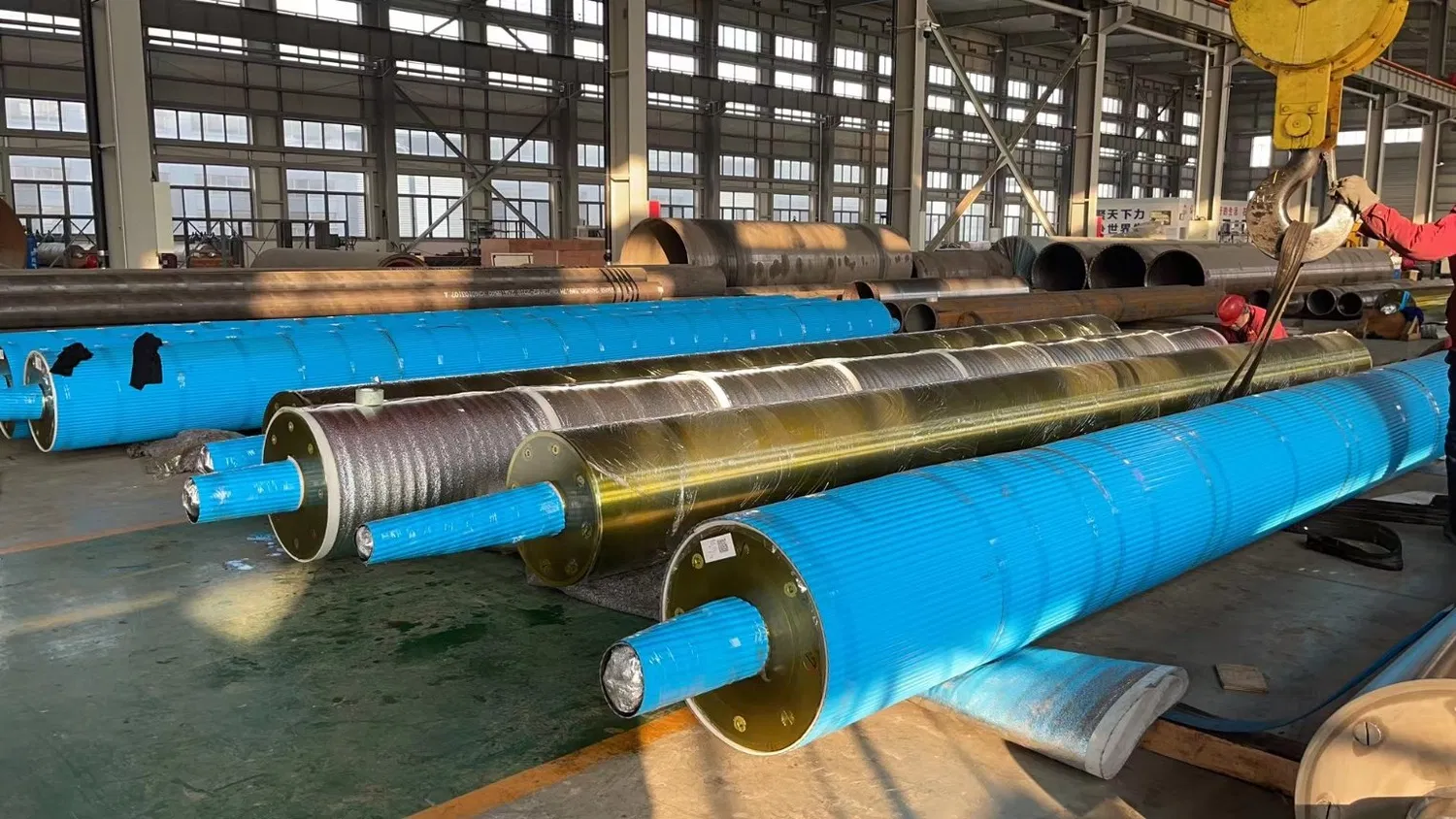

4. Metal Coatings
While less common for direct paper contact in many sections, certain metal coatings or treatments are used for specific roll types or as a base for other coatings.
- Hard Chrome: Offers good hardness and wear resistance but can be susceptible to corrosion and may not be ideal for all paper grades due to potential marking.
- Stainless Steel: Used for corrosion resistance, particularly in wet end applications.
These are often selected for their robustness and specific resistance properties rather than for surface finish characteristics.
The Process of Selecting and Implementing Roll Coatings
Selecting the right coating is only half the battle. Proper implementation and ongoing management are equally vital for ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
1. Needs Assessment and Consultation
The first step is a thorough assessment of your current situation and future needs. This involves:
- Analyzing Current Performance: Identify any issues with existing roll coatings – wear rates, sticking, marking, downtime.
- Defining Performance Goals: What do you want to achieve? Increased speed? Better paper quality? Reduced downtime?
- Consulting Experts: Engage with reputable coating manufacturers and application specialists. They possess invaluable knowledge and can guide you through the complex options. This is a crucial step in any effective guide to selecting paper machine roll coatings.
Have you ever wondered why one mill experiences fewer roll-related issues than another? Often, it comes down to this meticulous needs assessment and expert consultation.
2. Material Testing and Specification
Once potential coatings are identified, rigorous testing is often recommended.
- Laboratory Testing: Simulating operational conditions to evaluate wear, adhesion, and chemical resistance.
- Field Trials: Implementing a new coating on a trial basis on one or more rolls to assess performance in the actual mill environment.
Clear specifications for the coating, including material composition, hardness, surface finish, and adhesion strength, are essential for ensuring consistency and quality from your chosen supplier.
3. Application and Quality Control
The quality of the coating application is as important as the coating material itself.
- Surface Preparation: Proper cleaning and preparation of the base roll are critical for achieving excellent adhesion.
- Application Method: Whether it's spraying, wrapping, or another method, it must be executed by skilled technicians using calibrated equipment.
- Quality Checks: Post-application checks, including visual inspection, hardness testing, and adhesion tests, are vital to ensure the coating meets specifications.
Frankly speaking, a poorly applied coating, no matter how good the material, will lead to premature failure.
4. Maintenance and Monitoring
Ongoing maintenance and monitoring are key to maximizing the lifespan of your roll coatings.
- Regular Inspections: Periodically inspect rolls for signs of wear, damage, or delamination.
- Proactive Refurbishment: Address minor issues before they become major problems. Refurbishing a coating can often be more cost-effective than a full replacement.
- Record Keeping: Maintain detailed records of coating applications, maintenance performed, and performance data. This information is invaluable for future selection and troubleshooting.
Understanding the lifecycle of your paper machine roll coatings is an ongoing process, not a one-time decision.
The Future of Paper Machine Roll Coatings
The paper industry is constantly evolving, driven by demands for higher quality, increased sustainability, and greater efficiency. This evolution is also shaping the future of roll coatings.
- Advanced Materials: Expect to see continued development in high-performance polymers, nanocomposites, and more durable ceramic formulations offering enhanced properties like self-healing or anti-microbial capabilities.
- Smart Coatings: The integration of sensors or responsive elements within coatings could allow for real-time monitoring of roll condition and paper web properties, enabling predictive maintenance and finer process control.
- Environmentally Friendly Options: As sustainability becomes even more critical, there will be a growing focus on coatings with lower environmental impact during manufacturing and application, as well as coatings that contribute to energy savings in the paper machine.
The drive for innovation in this area is relentless, ensuring that paper manufacturers will have even more sophisticated tools at their disposal to optimize their operations.
In conclusion, selecting the right paper machine roll coatings is a multifaceted process that demands a deep understanding of materials, operational conditions, and economic factors. By approaching this decision with a thorough needs assessment, expert consultation, and a focus on lifecycle value, you can significantly enhance your paper production efficiency, quality, and profitability.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website:paper machine roll coatings
About the author: With over 15 years of hands-on experience in paper manufacturing and machinery optimization, Alex Chen is a recognized expert in paper machine component engineering. His work focuses on enhancing operational efficiency and product quality through advanced material science and strategic equipment selection. Alex is passionate about sharing his insights to help the industry thrive.