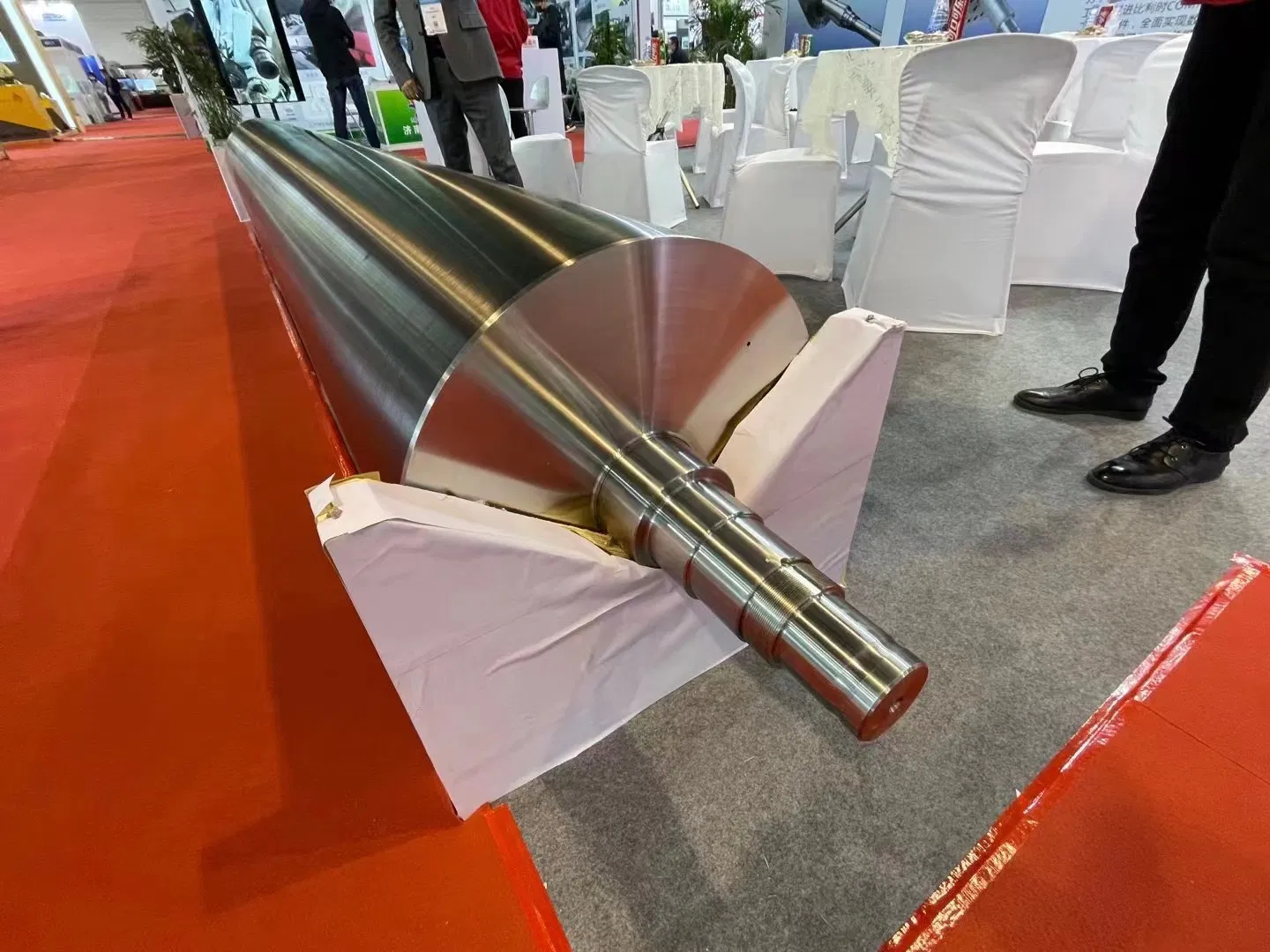
In the complex world of paper manufacturing, every stage of the process is vital, but few are as energy-intensive and critical to final product quality as drying. At the heart of the drying section lies a component that quietly performs under immense stress: the paper machine dryer cylinder. These large, heated vessels are responsible for removing the vast majority of water from the paper web, transforming it from a fragile, wet sheet into a stable, usable material. Understanding the nuances of these cylinders – their design, operation, maintenance, and potential issues – is paramount for any mill looking to optimize efficiency, reduce costs, and maintain consistent product quality. Frankly speaking, without effectively functioning dryer cylinders, producing high-quality paper at speed would be impossible. Their performance directly impacts machine runnability, energy consumption, and ultimately, the bottom line.
The Crucial Role and Basic Anatomy
So, what exactly is a paper machine dryer cylinder? Essentially, it's a hollow cylindrical shell, typically made from cast iron or sometimes steel, designed to be heated internally, usually by steam. The paper web wraps around the outer surface of these rotating cylinders, and heat is transferred from the cylinder wall through the paper, evaporating the remaining water. This process is far more complex than it sounds. Internally, a sophisticated steam and condensate system manages the flow of steam in and hot water out. Externally, the surface must be incredibly smooth and uniform to ensure even contact with the paper web and efficient heat transfer without damaging the delicate sheet. These cylinders operate under demanding conditions – high temperatures (often exceeding 150°C), significant internal pressures, and the constant friction of the paper web and felt. Their structural integrity and surface condition are non-negotiable for safe and efficient operation. Interestingly enough, while their basic function seems simple, the engineering behind maintaining uniform temperature across a large, rotating metal shell is quite intricate.
Different Strokes: Types and Materials
Not all dryer cylinders are created equal; their design and materials vary depending on the specific requirements of the paper machine and the paper grades being produced. The most common material for traditional cylinders is high-quality cast iron, specifically engineered to withstand thermal stresses and pressure. Cast iron offers good heat retention properties and machinability. However, steel cylinders, particularly for higher speeds and pressures, are also used, offering potentially greater strength and thinner walls for faster heat response. Within these materials, designs can vary: single-shell cylinders are simpler, while double-shell cylinders incorporate internal ribbing or channels to promote turbulence in the steam flow, enhancing heat transfer and potentially improving drying uniformity. Surface coatings, such as chrome plating or specialized polymer-ceramic composites, can be applied to the outer surface to improve release properties, enhance wear resistance, or alter surface energy. Selecting the appropriate type and material for a given position in the dryer section requires careful consideration of speed, temperature, pressure, and the type of paper being manufactured.
Mastering the Heat: The Drying Process Mechanism
Understanding *how* these cylinders dry paper is key to optimizing the process. Heat transfer is the primary mechanism. Steam introduced into the cylinder condenses on the inner surface, releasing latent heat. This heat then conducts through the cylinder wall to the outer surface. When the paper web comes into contact with the hot surface, this heat is transferred to the water within the web, causing it to evaporate. The resulting water vapor then moves away from the cylinder surface and is typically carried away by air circulation or captured by hood ventilation systems. Efficient heat transfer relies on several factors: the temperature difference between the steam and the paper, the thermal conductivity of the cylinder material, the cleanliness and smoothness of the cylinder surface, and importantly, effective removal of condensate from inside the cylinder. Accumulated condensate forms a water ring that acts as an insulator, significantly reducing heat transfer efficiency. This is why internal design and steam system management are just as crucial as the external cylinder surface.
Factors Dictating Performance
Several critical factors dictate the performance and efficiency of a paper machine dryer cylinder. Firstly, the surface condition is paramount. A smooth, clean, and uniform surface ensures maximum contact with the paper web, facilitating optimal heat transfer and preventing sheet sticking or damage. Surface roughness, pitting, or deposits can severely hinder drying and impact paper quality. Secondly, the internal steam distribution and condensate removal system are vital. Even steam flow ensures uniform heating across the cylinder width, while efficient removal of hot condensate prevents insulating water rings. Modern systems often use siphons and blow-through steam to achieve this. Thirdly, the cylinder shell thickness and material properties influence heat conduction. Finally, operating parameters like steam pressure and temperature must be precisely controlled. Any variation in these factors can lead to uneven drying profiles across the paper web, resulting in moisture variations that affect strength, printability, and runnability in subsequent processes. Have you ever wondered why moisture streaks appear in paper? Often, it traces back to uneven heat transfer from a dryer cylinder.
Confronting the Common Challenges
Despite their robust construction, paper machine dryer cylinders face a number of challenges in their demanding environment. Corrosion, both internal (from aggressive condensate) and external (from process chemicals or ambient conditions), is a constant threat to structural integrity. Cracking, particularly near stress points or due to thermal cycling, is a serious safety concern requiring immediate attention. Wear on the outer surface from constant friction with the paper web and dryer felts can alter the surface profile and finish, impairing heat transfer and potentially causing sheet breaks. Surface defects like pitting, scaling, or deposits can also form, leading to uneven drying and quality issues. Uneven temperature profiles across the cylinder face can be caused by issues with steam distribution, condensate removal, or internal deposits. Addressing these challenges requires proactive monitoring and maintenance strategies. Ignoring these issues can lead to reduced drying capacity, increased energy consumption, more frequent sheet breaks, and ultimately, costly downtime and potential safety hazards.
The Cornerstone: Proactive Maintenance and Inspection
Given their critical role and the stresses they endure, proactive maintenance and regular inspection of paper machine dryer cylinders are absolutely non-negotiable. Routine visual inspections can reveal external wear, corrosion, or surface defects. More advanced techniques are essential for assessing internal condition and structural integrity. Non-destructive testing (NDT) methods, such as ultrasonic testing (UT) to measure shell thickness and detect internal flaws, magnetic particle testing (MT) to find surface cracks, and phased array ultrasonic testing (PAUT) for detailed internal crack detection, are crucial. Periodic surface grinding or polishing may be necessary to restore the desired surface finish and profile. Internal cleaning can remove deposits and scale that impede heat transfer and condensate flow. Monitoring steam pressure, temperature, and condensate return rates provides valuable insights into the operational health of the cylinder and its associated systems. A well-planned maintenance program, including regular NDT, surface care, and system monitoring, can significantly extend the lifespan of dryer cylinders and prevent unexpected failures.
Boosting Efficiency: Optimization Strategies
Simply maintaining the status quo isn't enough in today's competitive paper market; optimizing the performance of your paper machine dryer cylinders is key to energy savings and increased throughput. Strategies for optimization often focus on improving heat transfer and drying uniformity. This can involve upgrading steam and condensate systems to ensure optimal steam distribution and efficient condensate removal, perhaps through high-performance siphons or blow-through systems. Improving hood ventilation and air circulation around the dryer section helps remove humid air, increasing the drying potential. Applying specialized surface coatings can improve heat transfer, enhance release properties, and reduce wear, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing maintenance needs. Ensuring proper felt tension and permeability is also crucial, as the felt helps hold the paper web firmly against the cylinder surface for better contact. Analyzing drying profiles using infrared cameras or moisture sensors can pinpoint areas of concern and guide targeted optimization efforts. Even small improvements in drying efficiency can translate into substantial energy cost reductions over time.
Selecting the Right Partner and Solution
When facing challenges with your paper machine dryer cylinder – whether it's declining efficiency, surface issues, structural concerns, or simply planning for the future – selecting the right partner for inspection, maintenance, repair, or even replacement is a critical decision. Expertise in metallurgy, steam systems, surface engineering, and non-destructive testing is essential. A good partner can provide accurate assessments of your current cylinder health, recommend appropriate maintenance or repair strategies, or guide you through the selection process for new or reconditioned cylinders if necessary. They should understand the specific demands of your machine and paper grades. In my experience, collaborating with specialists who possess deep knowledge of paper machine components and processes leads to the most effective and lasting solutions. It's not just about fixing a problem; it's about implementing solutions that enhance long-term performance and reliability.
Addressing Your Dryer Cylinder Needs
Reliability and efficiency in the drying section are not optional; they are fundamental to profitability. Issues with a paper machine dryer cylinder can quickly cascade into production bottlenecks, quality defects, excessive energy consumption, and even safety risks. That's where specialized services come into play. Our company understands the intricacies of these vital components. We offer a range of services designed to address the specific challenges mills face, from comprehensive inspection and non-destructive testing to precision surface grinding, internal cleaning, and expert guidance on steam and condensate system optimization. Whether you require a detailed assessment of a single cylinder, a preventative maintenance program for your entire dryer section, or assistance with planning an upgrade, we have the expertise and technology to help you achieve peak drying performance. We focus on providing practical, actionable solutions tailored to your operational needs and budget.
Moving Forward with Confidence
The paper machine dryer cylinder is a workhorse of the paper industry, quietly enabling the transformation of wet pulp into finished paper. Its efficient and reliable operation is non-negotiable for a productive and profitable paper mill. By prioritizing proactive maintenance, utilizing advanced inspection techniques, and implementing targeted optimization strategies, mills can significantly extend the life of their dryer cylinders, reduce energy consumption, minimize downtime, and ensure consistent paper quality. Don't wait for a critical failure; regular assessment and care are key to preventing costly disruptions. Taking these steps allows you to move forward with confidence in the heart of your paper machine's drying section. What steps are you taking today to ensure the long-term health and performance of your dryer cylinders?
For more detailed information, please visit our official website: paper machine dryer cylinder