The hum of a paper machine is a symphony of precision engineering, a complex ballet of rollers working in unison to transform pulp into the paper we use every day. But like any finely tuned instrument, these machines experience wear and tear. Among the most critical components susceptible to this is the vast array of rolls. Understanding and diagnosing paper machine roll wear is not just about preventing costly breakdowns; it's fundamental to maintaining paper quality, optimizing production efficiency, and ensuring the longevity of your machinery. Frankly speaking, neglecting roll wear is a direct route to production headaches and financial losses.
The Silent Culprits: Understanding the Causes of Roll Wear
Roll wear isn't a singular event; it's often the culmination of several interacting factors. To effectively diagnose and address it, we first need to understand what's causing the problem. In my experience, the most common culprits fall into a few key categories.
Mechanical Stress and Abrasion
This is perhaps the most obvious cause. The constant contact with paper stock, chemicals, and even the environment itself can lead to abrasive wear. Think of it like rubbing a surface with sandpaper, repeatedly. Over time, this friction erodes the roll surface, leading to a loss of its intended profile and texture. This is particularly true for rolls in high-pressure zones or those handling abrasive materials.
Chemical Attack
The chemicals used in the papermaking process – from sizing agents to bleaching chemicals – can be aggressive. If the roll material isn't properly selected or if there are inconsistencies in the protective coatings, these chemicals can corrode or degrade the roll surface. This type of wear can be insidious, often manifesting as pitting or uneven etching that's not immediately visible.
Thermal Degradation
Some paper machine processes involve elevated temperatures. Prolonged exposure to heat can alter the material properties of the roll, making it more susceptible to mechanical wear or even causing surface fatigue. This is especially relevant in dryer sections where rolls operate at higher temperatures for extended periods.
Improper Loading and Alignment
Uneven or excessive pressure applied to rolls can create localized stress points, leading to accelerated wear in specific areas. Similarly, misalignment between rolls can cause them to grind against each other or the paper web in an unnatural way, significantly increasing wear rates. It's worth noting that even slight misalignments can have a profound impact over time.
Contamination and Debris
Foreign particles, such as grit, metal fragments, or even hardened pulp deposits, can get caught between rolls or between a roll and the paper web. These act like tiny grinding agents, causing scratches and gouges that compromise the roll surface.
Detecting the Unseen: Essential Paper Machine Roll Wear Diagnostics Techniques
Once we understand the potential causes, the next crucial step is effective paper machine roll wear diagnostics. Early detection is key to preventing minor issues from escalating into major problems. Interestingly enough, a combination of visual inspection, measurement, and advanced monitoring techniques yields the best results.
Visual Inspection: The First Line of Defense
This might sound basic, but regular, thorough visual inspections are invaluable. Operators and maintenance personnel should be trained to look for obvious signs of wear, such as:
- Surface imperfections: Scratches, pitting, gouges, or discoloration.
- Edge wear: Noticeable rounding or erosion at the edges of the roll.
- Deposit buildup: Uneven accumulation of material that can indicate underlying surface issues.
- Cracking or spalling: More severe forms of surface damage.
While visual inspection can identify overt problems, it often misses the subtle, early stages of wear.
Dimensional and Profile Measurement
This is where precision comes into play. Using tools like micrometers, profilometers, or laser scanners, maintenance teams can accurately measure the diameter and profile of the rolls. Deviations from the original specifications are clear indicators of wear. A worn roll won't have the consistent diameter or the precise crown (slight bulge in the center) required for even pressure distribution across the paper web.
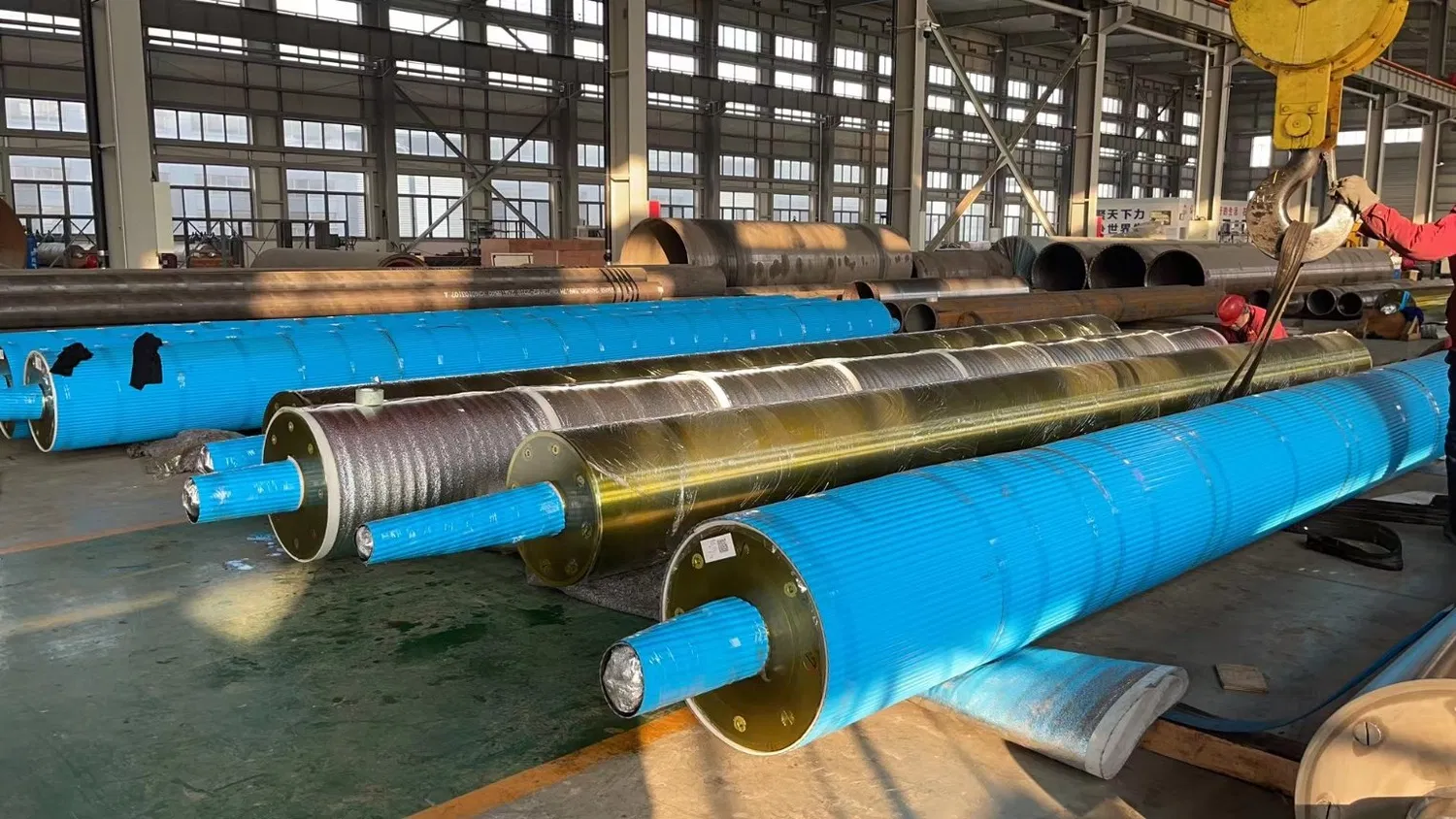

This type of measurement is critical for understanding how the roll's geometry has changed and the potential impact on paper formation and sheet flatness.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) Methods
For a deeper understanding of the roll's internal condition and surface integrity without causing damage, NDT methods are employed.
- Ultrasonic testing: Can detect internal flaws, cracks, or delamination within the roll material.
- Eddy current testing: Effective for identifying surface cracks and subsurface defects in conductive materials.
- Dye penetrant testing: A simple yet effective method for revealing surface-breaking cracks.
These techniques are vital for assessing the structural integrity of the roll, especially after a period of operation or if suspecting internal damage.
Vibration Analysis
Rolls are rotating components, and their condition directly influences the vibration signatures of the paper machine. An increase in specific vibration frequencies or amplitudes can indicate:
- Imbalance: Often caused by uneven wear or material buildup.
- Bearing issues: While not direct roll wear, worn bearings can lead to eccentric rotation and accelerated roll wear.
- Surface irregularities: Worn or damaged roll surfaces can create distinct vibration patterns.
Monitoring vibration patterns over time allows for the detection of developing issues before they become catastrophic. This is a cornerstone of proactive maintenance.
Thermography
Infrared cameras can detect temperature anomalies on the surface of the rolls. Uneven heating or hot spots can indicate:
- Friction: Areas of increased friction due to wear or debris.
- Improper lubrication: Leading to increased heat generation.
- Internal defects: Causing localized temperature changes.
Thermography provides a visual map of thermal conditions, highlighting areas that require further investigation.
Proactive Strategies: Preventing and Managing Roll Wear
The ultimate goal of paper machine roll wear diagnostics is to move from reactive repairs to proactive prevention. By implementing robust maintenance strategies, you can significantly extend the life of your rolls and minimize downtime.
Material Selection and Surface Treatments
Choosing the right materials and surface treatments for your rolls is paramount. Depending on the specific application and the chemicals involved, options range from hardened steels and specialized alloys to advanced composite materials and ceramic coatings. These treatments are designed to resist abrasion, corrosion, and thermal degradation. For instance, a rubber-covered roll will have different wear characteristics and require different diagnostic approaches than a polished steel calender roll.
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance Schedules
A consistent cleaning regimen is essential. Removing pulp deposits, chemical residues, and foreign debris prevents them from acting as abrasive agents. Implementing a strict schedule for roll cleaning, lubrication, and inspection ensures that potential issues are addressed before they cause significant wear.
Optimized Operating Parameters
Ensuring that rolls are operating within their designed parameters – including pressure, speed, and temperature – is critical. Regularly reviewing and adjusting these parameters based on the paper grade being produced and the condition of the machine can prevent excessive stress on the rolls.
Condition Monitoring Systems
Investing in advanced condition monitoring systems that integrate data from vibration sensors, temperature probes, and dimensional scanners can provide real-time insights into roll health. These systems can alert maintenance teams to deviations from normal operating conditions, allowing for timely intervention. This integrated approach to paper machine roll wear diagnostics is becoming increasingly sophisticated.
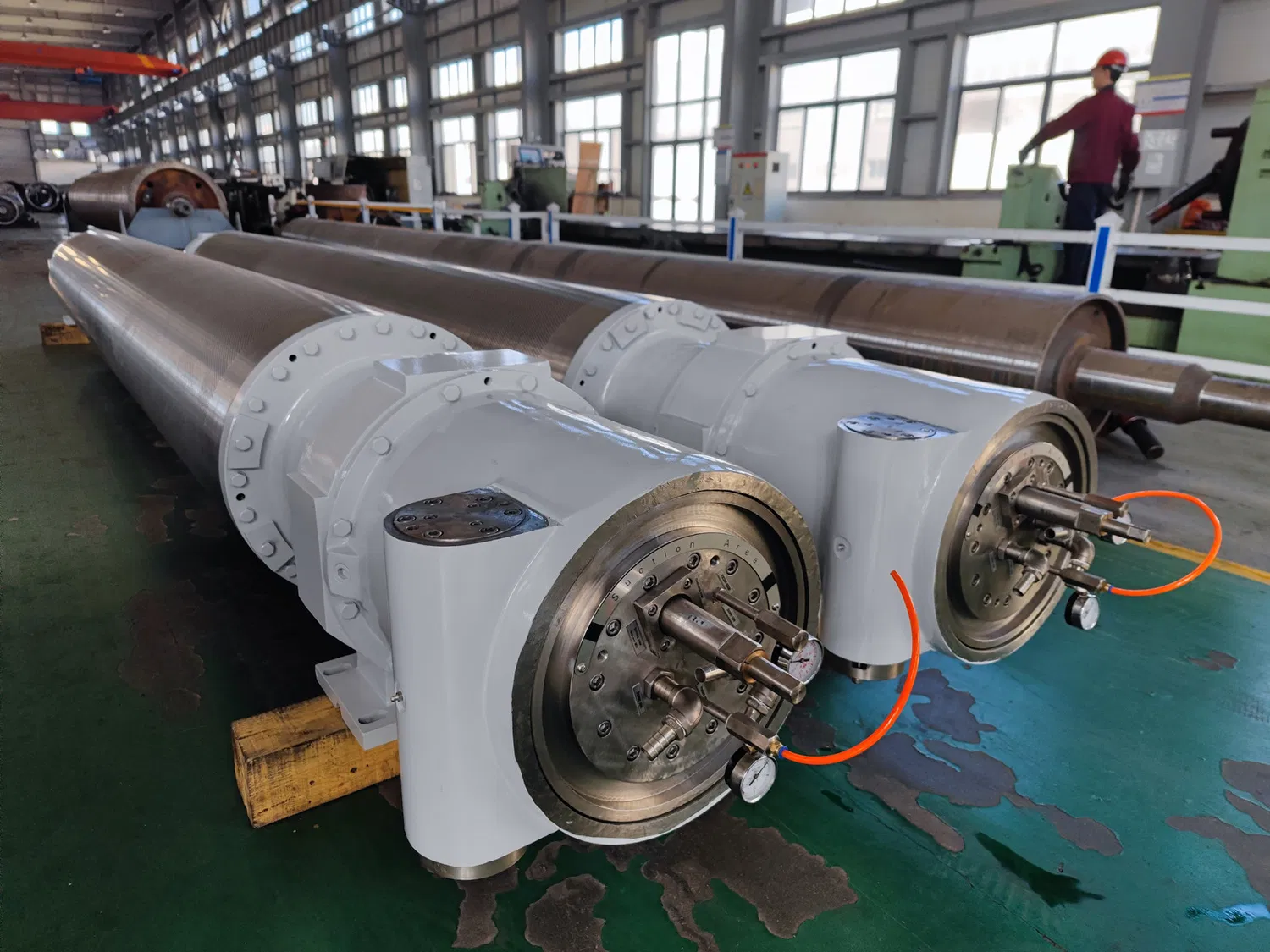

Planned Refurbishment and Replacement
Even with the best preventative measures, rolls will eventually wear out. Establishing a planned refurbishment or replacement schedule based on historical data, wear trends, and diagnostic findings is more cost-effective than waiting for a failure. This allows for scheduled downtime and minimizes unexpected production losses.
The Impact of Roll Wear on Paper Quality
It's easy to focus solely on the mechanical aspects of roll wear, but its impact on the final product – the paper itself – is profound. Have you ever wondered why paper quality can fluctuate? Roll wear is often a silent contributor.
Surface Defects
Worn or damaged rolls can impart surface defects onto the paper web. Scratches, pits, and uneven textures from worn rolls can lead to:
- Coating inconsistencies: Affecting printability and appearance.
- Roughness issues: Impacting tactile feel and performance in applications like packaging.
- Visual imperfections: Such as streaks or blemishes that reduce the aesthetic appeal.
Dimensional Stability and Flatness
The crown and surface profile of rolls are critical for applying uniform pressure across the width of the paper web. As rolls wear, their profile changes, leading to uneven moisture profiles and reduced dimensional stability. This can result in issues like curling, cockling, and poor sheet flatness, which are particularly problematic in high-speed printing and converting operations.
Web Breaks and Production Downtime
Severely worn or damaged rolls can create points of weakness in the paper web, increasing the likelihood of web breaks. These breaks are incredibly costly, leading to significant production downtime, material waste, and safety hazards. Effective paper machine roll wear diagnostics directly contributes to reducing these costly interruptions.
Energy Consumption
Interestingly enough, worn rolls can sometimes lead to increased energy consumption. For example, if a press roll is worn and not applying uniform pressure, the dryer section might need to work harder to remove residual moisture, consuming more energy.
The Future of Roll Wear Diagnostics
The field of paper machine roll wear diagnostics is continuously evolving. We're seeing a greater integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) into condition monitoring systems. These advanced technologies can analyze vast amounts of sensor data, identify subtle patterns indicative of wear that might be missed by human operators, and predict potential failures with greater accuracy. Predictive maintenance, powered by AI, is no longer a futuristic concept but a present-day reality for many forward-thinking paper mills. The goal is to move beyond simply diagnosing wear to predicting it long before it impacts production.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website:paper machine roll wear diagnostics
About the author: Alex Chen is a seasoned mechanical engineer with over 15 years of experience in industrial maintenance and asset management. His expertise lies in the diagnostics and prognostics of rotating machinery, with a particular focus on the paper and pulp industry. Alex is passionate about leveraging advanced monitoring techniques to optimize equipment reliability and reduce operational costs. He believes in a proactive approach to maintenance, emphasizing the importance of understanding machine behavior to prevent failures.