When it comes to the intricate world of papermaking, every component plays a crucial role in the final product's quality and the machine's overall efficiency. Among these, paper machine rolls stand out as silent workhorses, constantly under immense stress from heat, pressure, chemicals, and abrasion. Frankly speaking, their material selection isn't just a technical detail; it's a strategic decision that directly impacts operational costs, product quality, and machine uptime. This comprehensive paper machine roll material selection guide aims to demystify the complexities, helping you make informed choices that drive success.
Have you ever wondered what goes into choosing the right material for a roll that might be spinning at thousands of feet per minute, handling tons of pulp, or drying paper at extreme temperatures? It's a fascinating blend of engineering, chemistry, and practical experience. In my experience, overlooking the nuances of material properties can lead to premature wear, costly downtime, and inconsistent paper quality. Let's dive deep into what makes a roll perform optimally.
Understanding the Critical Role of Paper Machine Rolls
A paper machine is a marvel of engineering, transforming a slurry of fibers into a finished paper product through a series of stages: forming, pressing, drying, calendering, and reeling. Each stage relies heavily on a variety of rolls, each with a specific function and, consequently, unique demands on its material. From the large, heavy press rolls that dewater the sheet to the delicate guide rolls that ensure proper web alignment, the choice of material is paramount.
To be honest, the performance of these rolls dictates the efficiency of the entire papermaking process. A roll that experiences excessive wear, corrosion, or deformation can lead to sheet breaks, uneven moisture profiles, poor surface finish, and ultimately, significant financial losses. This is precisely why a meticulous approach to the paper machine roll material selection guide is not just recommended, but essential. It's about ensuring reliability and maximizing the return on investment for these critical assets.
Key Factors Influencing Material Selection
Selecting the ideal material for a paper machine roll is far from a one-size-fits-all scenario. It involves a careful evaluation of several interconnected factors, each contributing to the roll's suitability for its specific application. Ignoring any of these can lead to suboptimal performance and a shortened lifespan.
Operating Conditions
The environment in which a roll operates is perhaps the most critical determinant of material choice.
- Temperature and Pressure: Dryer cylinders, for instance, must withstand high temperatures and steam pressure, necessitating materials with excellent thermal stability and strength. Press rolls, on the other hand, endure immense nip pressures and often elevated temperatures from dewatering.
- Chemical Environment: Papermaking processes often involve various chemicals, including acids, alkalis, bleaching agents, and sizing chemicals. Rolls exposed to these substances require materials with superior corrosion resistance. Stainless steels or specialized polymer covers are often chosen for such environments.
- Speed and Load: High-speed machines demand rolls with excellent dynamic balance and materials capable of resisting fatigue and deformation under continuous, high-stress rotation. The load on the roll also dictates the required mechanical strength and stiffness of the material.
Roll Function and Position
Each section of the paper machine places unique demands on its rolls.
- Forming Section: Rolls here are often exposed to abrasive fiber slurries and water. Materials need good wear resistance and corrosion resistance.
- Press Section: These rolls are critical for dewatering and need to withstand high nip pressures. They require excellent mechanical strength, stiffness, and often a specific surface hardness or cover for optimal water removal and sheet integrity.
- Dryer Section: Dryer cylinders are large, hollow rolls heated internally by steam. They must have high thermal conductivity, strength at elevated temperatures, and resistance to corrosion from condensate.
- Calender and Reel Sections: Rolls in these sections influence the final paper's surface properties (smoothness, gloss) and winding. They require excellent surface finish, hardness, and dimensional stability.
Desired Performance Characteristics
Beyond the operational environment, specific performance attributes are sought after.
- Wear Resistance: Crucial for rolls exposed to abrasive slurries or high friction.
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential in chemically aggressive environments.
- Thermal Stability and Conductivity: Important for dryer cylinders and rolls where temperature control is critical.
- Surface Finish and Release Properties: Affects paper quality and prevents sticking.
- Dynamic Balance and Stiffness: Critical for high-speed operations to prevent vibrations and ensure consistent nip profiles.
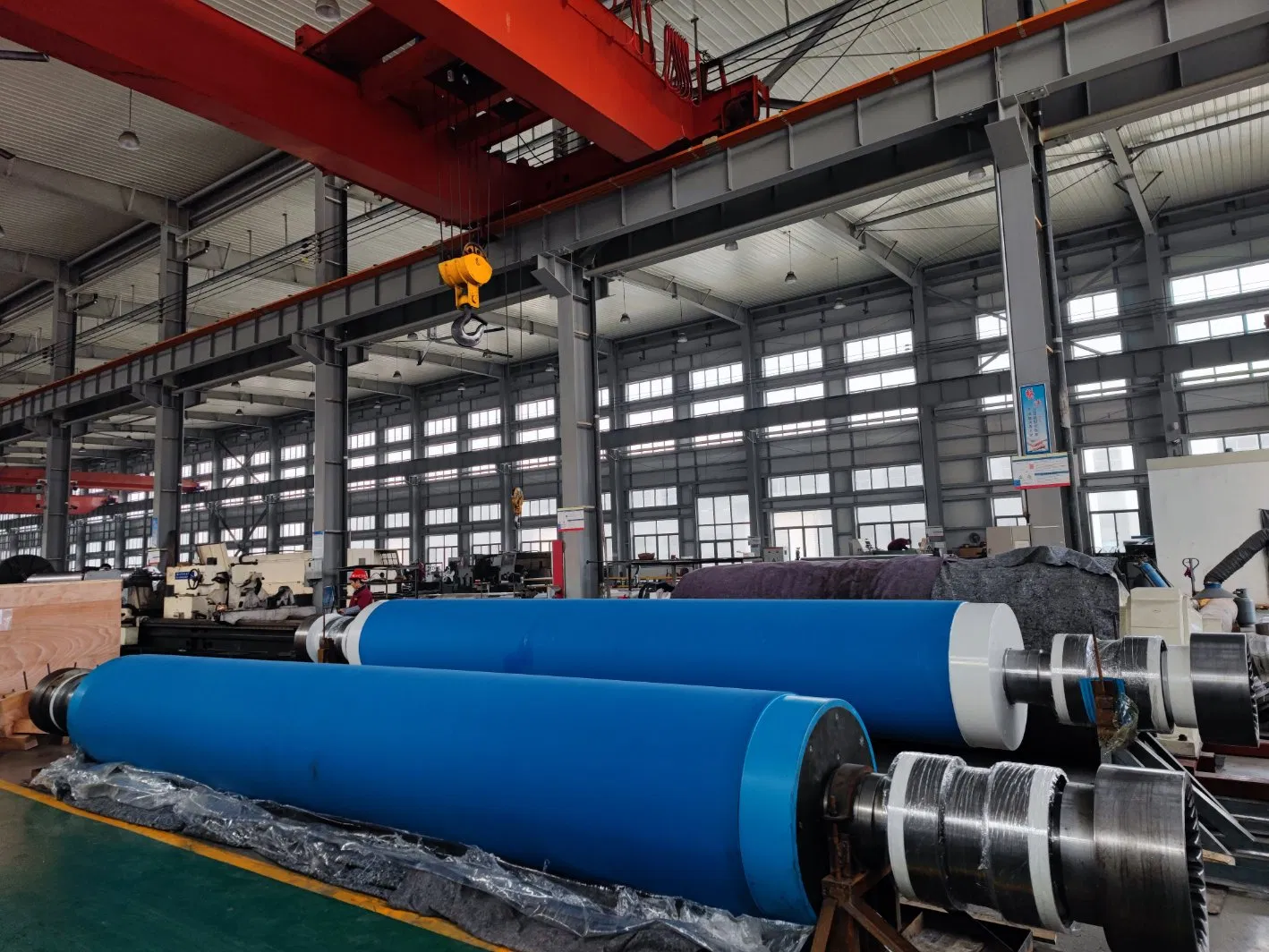

Common Roll Materials and Their Applications
The range of materials used for paper machine rolls is extensive, each offering a unique set of properties. Understanding these is fundamental to any effective paper machine roll material selection guide.
Cast Iron and Ductile Iron
Cast iron has historically been a workhorse in the paper industry, particularly for dryer cylinders due to its good thermal conductivity and ability to withstand high temperatures and pressures. Ductile iron, a form of cast iron with improved ductility and strength, is also used for certain structural components and rolls where higher mechanical properties are needed. Its cost-effectiveness and proven track record make it a popular choice, especially for the large, heavy dryer rolls.
Steel Alloys (Carbon, Stainless, Alloy Steels)
Steel alloys are widely used across various sections of the paper machine due to their superior strength, toughness, and versatility.
- Carbon Steel: Often used for core shafts, and sometimes for less demanding rolls where corrosion is not a major concern. It's strong and relatively inexpensive.
- Stainless Steel: Absolutely essential for rolls in wet sections (forming, press) and areas exposed to corrosive chemicals. Its excellent corrosion resistance, especially grades like 304 and 316, makes it ideal for suction rolls, press roll bodies, and guide rolls.
- Alloy Steels: These steels, containing elements like chromium, nickel, molybdenum, or vanadium, offer enhanced properties such as higher strength, hardness, and wear resistance. They are often used for calender rolls, where surface hardness and dimensional stability are critical, or for high-load press rolls.
Rubber and Polymer Covers
While the roll body might be metal, many rolls, particularly in the press and wet sections, are covered with a layer of rubber or polymer. These covers are crucial for achieving specific nip characteristics, dewatering efficiency, and protecting the roll body.
- Natural Rubber: Offers good elasticity and resilience, often used for guide rolls or felt rolls.
- Synthetic Rubbers (e.g., EPDM, Neoprene, Butyl): Provide improved resistance to chemicals, heat, and abrasion compared to natural rubber, making them suitable for various press and felt rolls.
- Polyurethane: Known for its excellent abrasion resistance, cut resistance, and load-bearing capacity. Polyurethane covers are increasingly popular for press rolls, size press rolls, and other applications requiring high durability and specific hardness.
Interestingly enough, the hardness and resilience of these covers are carefully selected based on the desired nip profile and dewatering efficiency. A well-chosen cover can significantly optimize paper machine roll performance.
Composite Materials
In recent years, composite materials have gained traction, especially for rolls where lightweight and high stiffness are advantageous.
- Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polymers (CFRP): Offer exceptional strength-to-weight ratios and stiffness. They are used for guide rolls, spreader rolls, and even some press rolls where reduced inertia and improved dynamic response are desired. Their lighter weight can also reduce energy consumption.
- Fiberglass Reinforced Polymers (FRP): A more economical composite, FRP rolls are also lightweight and corrosion-resistant, suitable for certain guide and felt rolls.
Many experts agree that the evolution of composite materials is a game-changer, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in roll design and contributing significantly to the depth of any modern paper machine roll material selection guide.
Advanced Coatings and Surface Treatments
Beyond the base material, surface coatings and treatments play an increasingly vital role in enhancing roll performance and extending lifespan. They can impart properties that the base material lacks, such as extreme hardness, superior release, or enhanced corrosion resistance. This is where the true art of optimizing paper machine roll performance often lies.
Thermal Spray Coatings (HVOF, Plasma Spray)
These processes involve spraying molten or semi-molten materials onto the roll surface, creating a dense, highly adherent coating.
- Ceramics (e.g., Chromium Oxide, Alumina): Provide exceptional wear resistance, hardness, and often good release properties. They are commonly used on calender rolls, dryer rolls, and even some press rolls.
- Carbides (e.g., Tungsten Carbide, Chromium Carbide): Offer extreme hardness and abrasion resistance, making them ideal for high-wear applications like suction roll journals, guide rolls, and certain press rolls.
- Metals and Alloys: Can be applied for corrosion resistance or specific surface textures.
Electroplating and Electroless Plating
These chemical processes deposit a layer of metal onto the roll surface.
- Hard Chrome Plating: Historically popular for its hardness, wear resistance, and low friction. Used on calender rolls, press rolls, and guide rolls. However, environmental concerns are leading to a search for alternatives.
- Electroless Nickel Plating: Provides excellent corrosion resistance and uniform thickness, even on complex geometries. It can be combined with other materials (e.g., PTFE) for enhanced release properties.
Polymer Coatings and Composites
Specialized polymer layers can be applied to rolls for specific functions. These are distinct from thick rubber/polymer covers.
- Fluoropolymer Coatings (e.g., PTFE): Known for their non-stick properties, ideal for release rolls in the dryer section or size press to prevent paper sticking.
- Specialized Polymer Composites: Engineered to provide a combination of properties like wear resistance, chemical resistance, and specific surface energy.
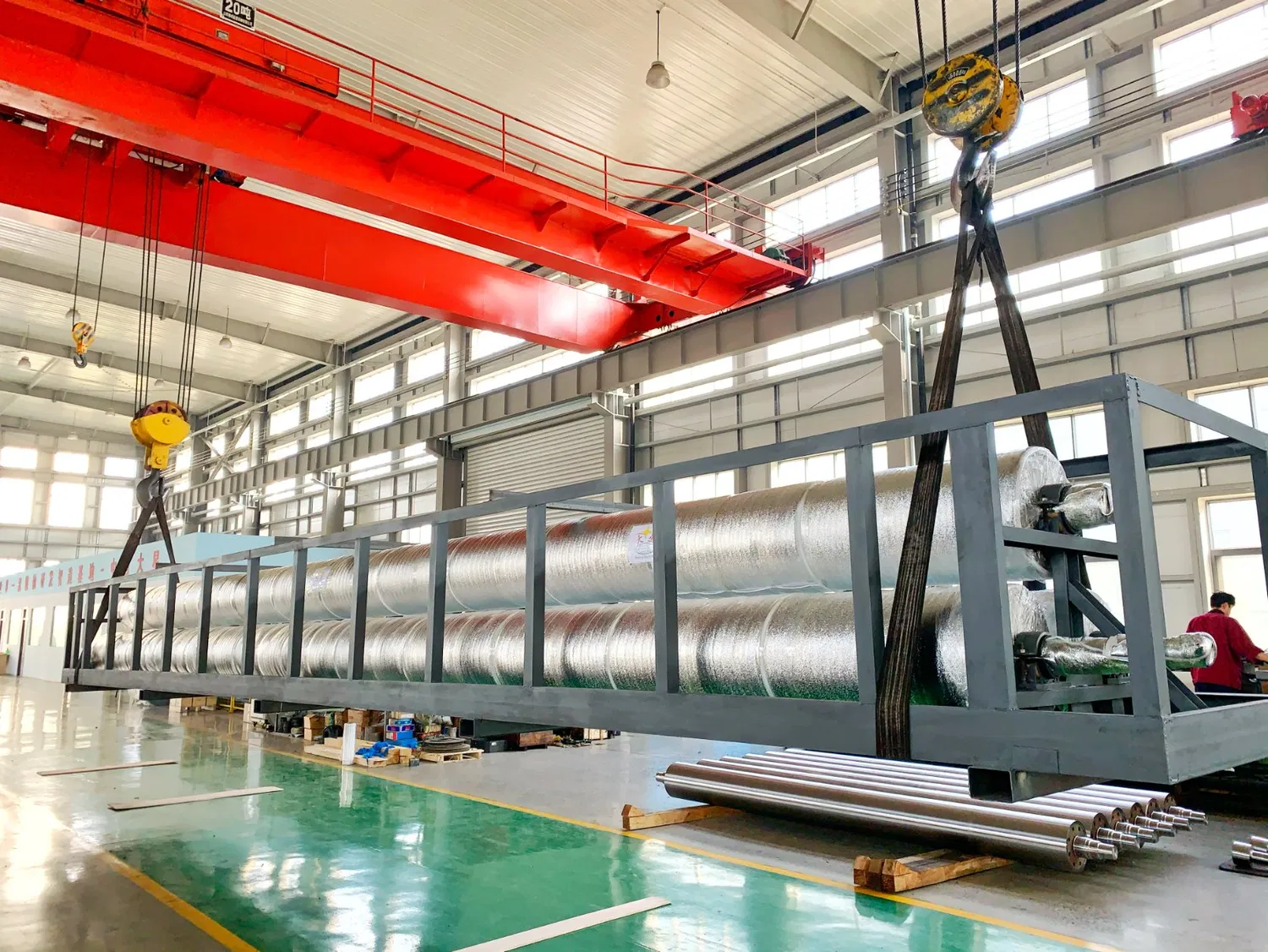

It's worth noting that these advanced coatings significantly enhance roll material durability in papermaking, allowing rolls to withstand harsher conditions and extend maintenance intervals. The right coating can be just as important as the base material itself.
Optimizing Roll Performance and Longevity
Choosing the right material is only the first step. To truly optimize roll performance and longevity, a holistic approach encompassing proper maintenance, operational awareness, and expert consultation is essential.
Material-Specific Maintenance Practices
Different materials and coatings require specific care.
- Grinding and Crown Management: Regular grinding is necessary to maintain the roll's precise geometry (crown) and surface finish, which are critical for uniform nip pressure and paper quality. The frequency and method depend heavily on the roll material and cover.
- Cleaning Protocols: Proper cleaning prevents buildup of fibers, fillers, and chemicals, which can cause uneven wear or surface damage. Cleaning agents and methods must be compatible with the roll material and coating.
- Inspection and Monitoring: Regular inspections for signs of wear, corrosion, cracking, or cover degradation are vital. Technologies like vibration analysis and thermal imaging can detect issues before they become critical failures.
- Re-covering and Re-coating: Knowing when to re-cover a rubber roll or re-coat a metal roll is key to preventing catastrophic failure and maintaining performance. This often involves specialized facilities and expertise.
Impact of Operational Changes
Changes in the papermaking process can significantly affect roll wear and performance.
- Paper Grade Changes: Switching between different paper grades (e.g., from fine paper to packaging board) can alter the load, abrasive nature of the furnish, or chemical environment, necessitating a re-evaluation of roll materials or maintenance schedules.
- Speed Increases: Running a machine faster puts more stress on rolls, increasing temperature and dynamic loads, which can accelerate wear if materials aren't up to the task.
- Chemical Adjustments: Changes in pH, use of new additives, or different bleaching sequences can impact the corrosion resistance requirements of rolls.
I've found that a proactive approach, anticipating how operational changes might affect roll integrity, is far more cost-effective than reacting to failures.
The Role of Expert Consultation
Frankly speaking, while this paper machine roll material selection guide provides a solid foundation, the nuances of real-world applications often require specialized knowledge. Engaging with experienced roll manufacturers, material scientists, or papermaking consultants can provide invaluable insights. They can help analyze specific operational challenges, recommend tailored material solutions, and advise on optimal maintenance strategies. Their expertise is crucial for truly optimizing paper machine roll performance and ensuring long-term reliability.
Conclusion: A Strategic Approach to Roll Material Selection
The journey through the world of paper machine roll material selection is complex but incredibly rewarding. It's clear that there's no single "best" material; instead, the optimal choice is always a careful balance of operational demands, environmental factors, desired performance characteristics, and economic considerations. From traditional cast iron to advanced composites and sophisticated surface coatings, each material plays a vital role in the intricate dance of papermaking.
By meticulously following the principles outlined in this paper machine roll material selection guide, and by continuously monitoring and adapting to changing conditions, paper mills can significantly enhance the longevity, efficiency, and overall performance of their machines. The future of papermaking relies not just on faster machines, but on smarter material choices that ensure sustainable and high-quality production. Investing time and resources into understanding and implementing the right material strategies for your rolls is, without a doubt, an investment in your mill's future success.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website:Paper machine roll materials
About the author: Mark Thompson is a seasoned expert in industrial machinery and materials science, with over two decades of experience specializing in the pulp and paper industry. His profound understanding of material properties, advanced coatings, and their application in demanding environments has helped numerous mills optimize their operations. Mark is passionate about sharing practical insights to enhance machine performance and longevity.