Frankly speaking, when you pick up a newspaper, a book, or even a simple tissue, do you ever stop to think about the journey that paper took to get into your hands? Most likely, you don't. Yet, behind every sheet of paper lies a complex, intricate process, and at the very heart of this process are components that, while often overlooked, are absolutely critical: the rolls for paper industry. These aren't just any rollers; they are precision-engineered workhorses that guide, press, and dry the paper web from a watery pulp into a finished product. To be honest, without them, modern paper production as we know it would simply grind to a halt.
The paper industry is a marvel of engineering, transforming raw wood fibers or recycled paper into a ubiquitous material essential for communication, packaging, and hygiene. And in this colossal operation, the various types of rolls play an indispensable role at every stage. From the initial dewatering of the pulp to the final smoothing and winding of the finished paper, each roll performs a specific, vital function. Have you ever wondered about the sheer force and precision required to handle a continuous web of paper moving at speeds of over 100 km/h? It's mind-boggling, and it’s a testament to the robust design and meticulous maintenance of these industrial paper mill rollers.
In my experience, many people outside the industry don't realize the complexity involved. They see paper as a simple commodity, but the machinery that produces it is anything but simple. The reliability and performance of these rolls directly impact the quality of the paper, the efficiency of the production line, and ultimately, the profitability of the mill. So, let's dive deeper into the world of these unsung heroes and uncover what makes them so vital.
The Pivotal Role of Rolls in Paper Manufacturing
The journey of paper begins as a slurry, mostly water, with a small percentage of fibers. This slurry is then transformed into a continuous sheet through a series of mechanical and thermal processes, all facilitated by an array of specialized rolls. Each section of a paper machine – from the wet end to the dry end – relies heavily on different types of rolls for specific tasks. It's worth noting that the demands on these rolls are immense: they must withstand extreme temperatures, high pressures, corrosive chemicals, and constant abrasion, all while maintaining precise dimensions and surface finishes.
Consider the sheer scale of operations in a modern paper mill. A single paper machine can be hundreds of meters long, processing tons of pulp per hour. The rolls within these machines are not just passive components; they are active participants in the paper-making process. They dewater the pulp, compact the sheet, transport it through various sections, and even impart specific surface characteristics. Without their precise function, the delicate balance of the paper-making process would be impossible to maintain. Many experts agree that the evolution of paper machine rolls manufacturing has been a key driver in the continuous improvement of paper quality and production speed over the decades.
Interestingly enough, the design and material science behind these rolls are constantly evolving. Engineers are always looking for ways to make them more durable, more efficient, and more resistant to the harsh operating environment. This continuous innovation ensures that the paper industry can meet the ever-growing global demand for paper products while striving for greater sustainability.
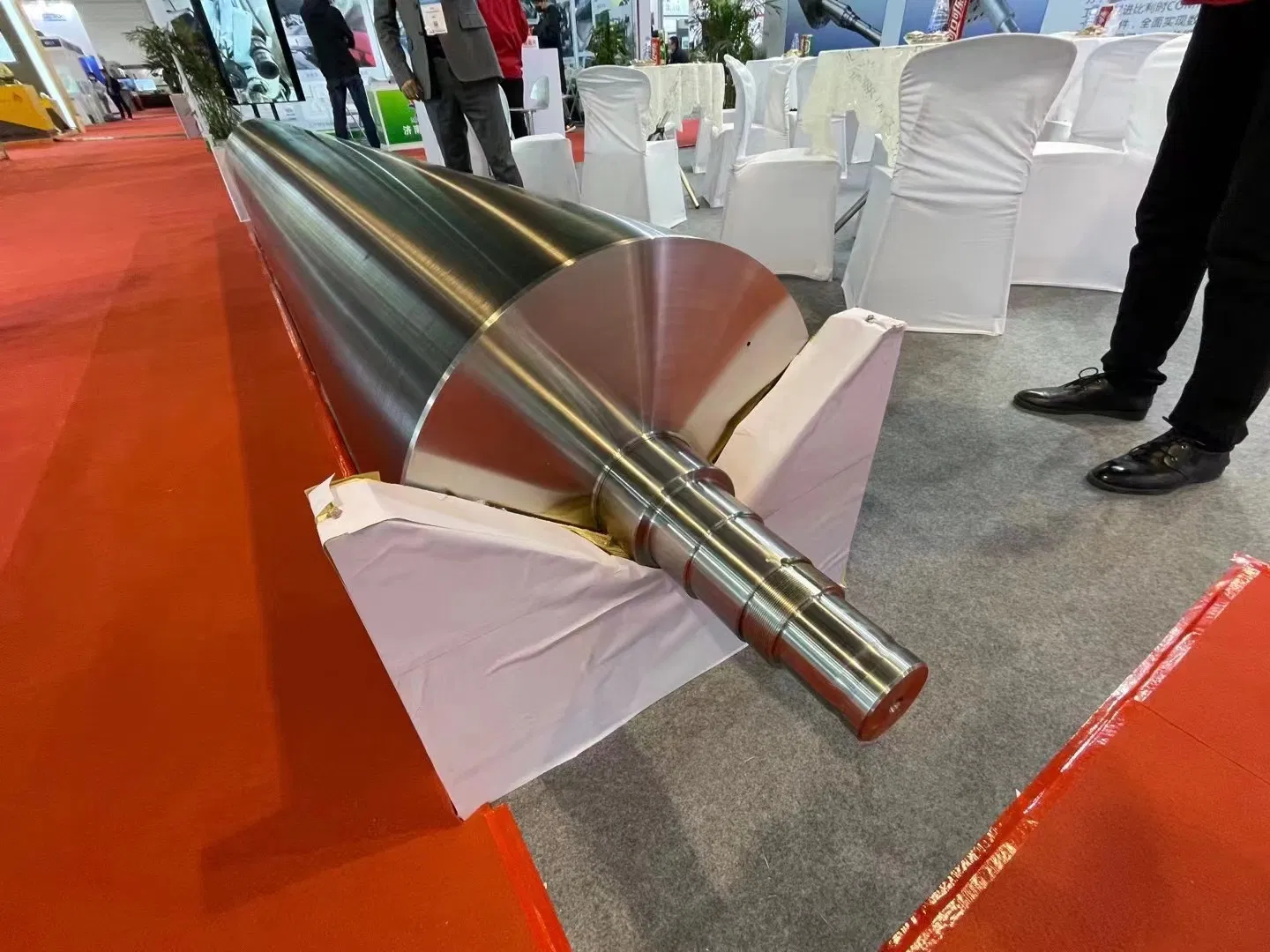

A Deep Dive into the Diverse Types of Rolls
The term "rolls for paper industry" encompasses a vast array of specialized components, each designed for a particular stage of the paper-making process. Understanding their distinct functions is key to appreciating their collective importance.
Forming Section Rolls
This is where the paper sheet truly begins to form. The pulp slurry is introduced onto a moving screen (wire), and gravity, along with suction, starts to remove water. Key rolls here include:
- Breast Rolls: Located at the very beginning of the forming section, these rolls support the forming fabric as the pulp slurry is delivered onto it. They need to be extremely stable and precise to ensure an even distribution of fibers.
- Couch Rolls: Positioned at the end of the forming section, these large, often perforated rolls use vacuum suction to remove a significant amount of water from the newly formed paper web, transferring it from the forming fabric to the press section. Their design is critical for effective dewatering without damaging the fragile web.
- Guide Rolls: Found throughout the machine, these rolls ensure the proper alignment and tension of the forming fabric and later, the felts. They are essential for smooth operation and preventing wrinkles or breaks in the web.
Press Section Rolls
After the forming section, the paper web is still very wet. The press section uses mechanical pressure to squeeze out more water, significantly increasing the dry content of the paper. This is a critical stage for energy efficiency, as removing water mechanically is far more energy-efficient than drying it with heat. Types of press rolls include:
- Suction Press Rolls: Similar to couch rolls, these rolls have a perforated shell and internal vacuum system to draw water out of the paper web as it passes through the nip (the point of contact between two rolls).
- Plain Press Rolls: These are solid rolls that apply direct pressure to the paper web, often in conjunction with a felt, to squeeze out water.
- Grooved Press Rolls: Featuring grooves on their surface, these rolls provide channels for water to escape, enhancing dewatering efficiency, especially at higher speeds.
- Felt Rolls: These rolls support and guide the press felts, which act as a cushion and absorb water pressed out of the paper web.
Dryer Section Rolls
Once the paper web leaves the press section, it enters the dryer section, which is typically the longest part of the paper machine. Here, steam-heated dryer cylinders evaporate the remaining water. These rolls operate at high temperatures and must be perfectly balanced to prevent vibrations and ensure uniform drying.
- Dryer Cylinders: Large, hollow, steam-heated cast iron or steel cylinders that transfer heat to the paper web, evaporating the water. Their surface finish is crucial for efficient heat transfer and preventing sticking.
- Dryer Felt Rolls: Guide and tension the dryer felts, which hold the paper web against the hot dryer cylinders to maximize heat transfer.
Calender and Reel Section Rolls
The final stages involve refining the paper's surface and winding it into large rolls.
- Calender Rolls: These rolls are used in the calender stack to smooth the paper, control its thickness, and impart desired surface properties like gloss or smoothness. They can be hard (steel or chilled cast iron) or soft (covered with elastic materials like rubber or composite). The precise nip pressure and temperature control here are vital for final paper quality.
- Reel Spools/Reel Drums: At the very end of the machine, the finished paper is wound onto large spools or a reel drum to create jumbo rolls, which are then further processed into smaller rolls or sheets.
The materials used for these rolls vary widely, from cast iron and steel to granite, rubber, and advanced composite materials, each chosen for its specific properties like hardness, wear resistance, heat conductivity, and chemical inertness. Surface coatings, such as chrome, ceramics, or polymers, are also frequently applied to enhance durability and performance.
The Meticulous Manufacturing Process of Paper Machine Rolls
The creation of high-quality rolls for paper industry is a testament to precision engineering and advanced metallurgy. It's not a simple casting and machining job; it's a highly specialized process that ensures these critical components can withstand the rigorous demands of continuous paper production. This is where paper machine rolls manufacturing truly shines, blending traditional craftsmanship with cutting-edge technology.
The process typically begins with the careful selection of raw materials. For larger rolls, high-grade cast iron or specialized steels are often used due to their strength and stability. Smaller rolls or those requiring specific surface properties might utilize different alloys or even composite materials. The casting or forging process is then meticulously controlled to ensure a uniform internal structure, free from defects that could compromise the roll's integrity under stress.
Once the basic form is achieved, the real precision work begins: machining and grinding. This stage is absolutely critical. The roll's surface must be machined to extremely tight tolerances, often within microns, to ensure perfect concentricity and a flawless surface finish. Any deviation can lead to uneven paper thickness, web breaks, or premature wear. Grinding is performed using specialized machinery that can achieve the required smoothness and geometrical accuracy, often under controlled temperature conditions to prevent thermal distortion.
After the primary machining, many rolls undergo a coating process. These coatings, which can include hard chrome, tungsten carbide, ceramics, or rubber, are applied to enhance wear resistance, corrosion protection, or specific surface properties like grip or release. The application of these coatings requires specialized techniques to ensure strong adhesion and uniform thickness. Finally, dynamic balancing is performed. Given the high rotational speeds at which these rolls operate, even a slight imbalance can lead to severe vibrations, impacting paper quality and potentially damaging the machine. Balancing ensures smooth, stable operation at all speeds.
Throughout the entire manufacturing process, rigorous quality control checks are performed at every stage. This includes ultrasonic testing for internal defects, dimensional checks, surface roughness measurements, and comprehensive performance tests. This meticulous attention to detail in paper machine rolls manufacturing is what differentiates a reliable, long-lasting roll from one that could cause costly downtime.
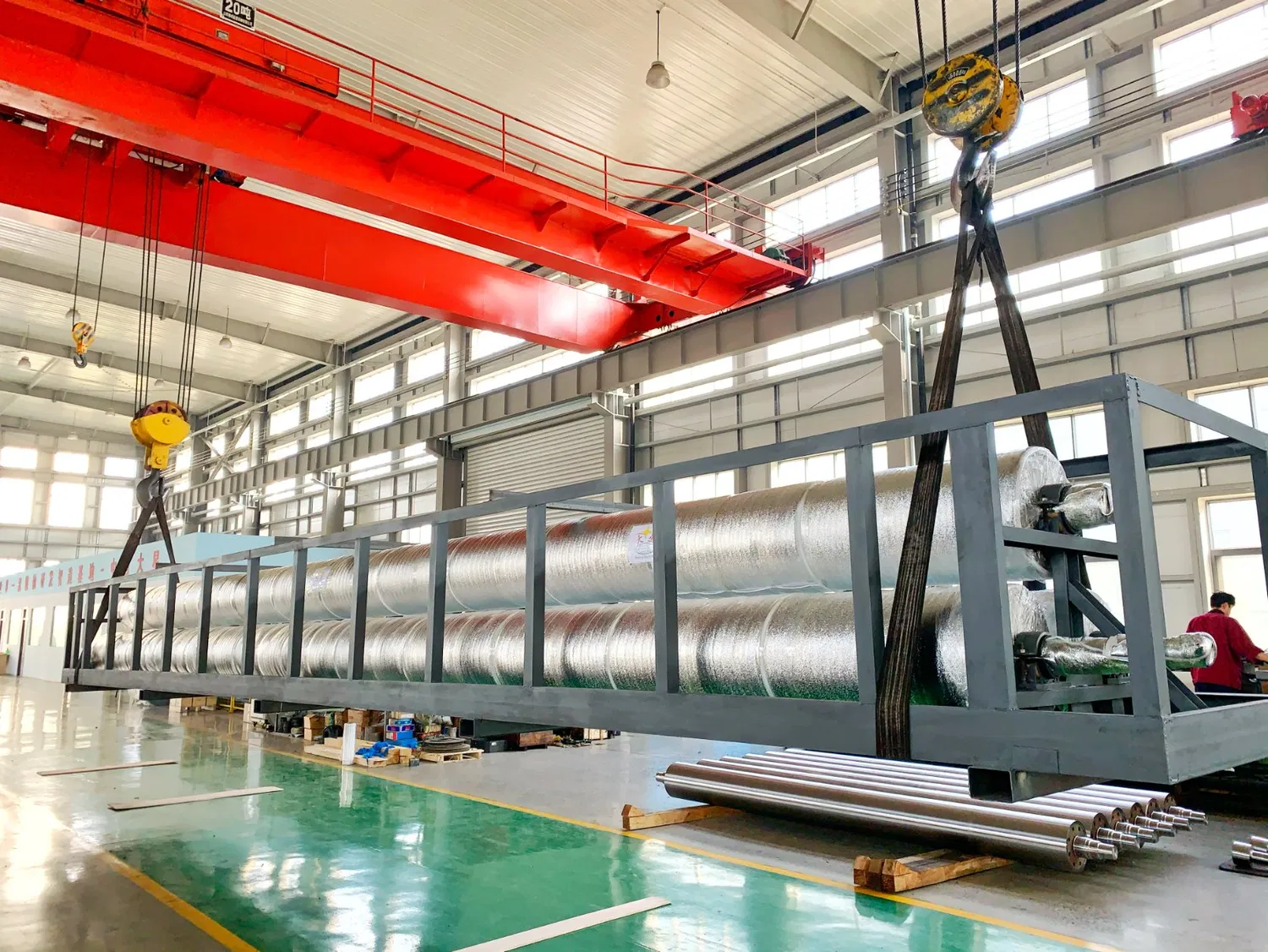

Ensuring Longevity: Maintenance and Operational Challenges
Even the most robust rolls for paper industry require diligent maintenance to ensure their longevity and optimal performance. The operating environment in a paper mill is notoriously harsh, characterized by high humidity, elevated temperatures, corrosive chemicals, and constant mechanical stress. Proactive maintenance is not just good practice; it’s a necessity to prevent costly unscheduled downtime and maintain product quality. This is where effective maintenance of paper machine rolls becomes paramount.
Regular inspection and cleaning are fundamental. Operators and maintenance crews routinely check for signs of wear, corrosion, pitting, or any surface damage. Even minor imperfections on a roll's surface can translate into defects on the paper web. Bearings, which allow the rolls to rotate smoothly, are another critical area. Proper lubrication, regular checks for wear, and timely replacement of bearings are essential to prevent catastrophic failures. A seized bearing can cause immense damage to a roll and halt production immediately.
One of the most common maintenance procedures for industrial paper mill rollers is roll grinding and resurfacing. Over time, the surfaces of rolls can become worn, grooved, or develop uneven profiles due to continuous contact with the paper web, felts, and pressing forces. Grinding involves removing a thin layer of material from the roll's surface to restore its original geometry and smoothness. This process requires specialized grinding machines and skilled technicians to ensure the correct crown (a slight taper or curve across the roll's width) is maintained, which is vital for uniform pressure distribution across the paper web.
Common operational challenges include:
- Wear and Abrasion: Constant contact with fibers, fillers, and other components leads to gradual wear of the roll surface.
- Corrosion: The presence of water, chemicals, and elevated temperatures can lead to corrosion, especially on unprotected metal surfaces.
- Deflection: Under immense pressure and weight, rolls can deflect, leading to uneven nips and inconsistent paper properties. Proper design and material selection minimize this, but it remains a factor.
- Vibration: Imbalance, bearing issues, or uneven wear can cause vibrations, which degrade paper quality and accelerate machine wear.
- Sticking: In the dryer section, paper can sometimes stick to the hot dryer cylinders, causing breaks and production stoppages.
Frankly speaking, investing in predictive maintenance technologies, such as vibration analysis, thermal imaging, and online monitoring systems, can significantly improve the lifespan and performance of rolls. These technologies allow mills to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems, enabling scheduled maintenance rather than reactive repairs. In my experience, a robust maintenance program is the single biggest factor in maximizing the uptime and efficiency of a paper machine.
The Future of Rolls: Innovations and Sustainable Practices
The paper industry, like many others, is constantly evolving, driven by demands for higher efficiency, better product quality, and increased sustainability. This push for innovation directly impacts the design and functionality of rolls for paper industry. The future promises even more advanced materials, smarter monitoring systems, and designs that contribute to a greener production process.
One significant area of innovation is the development of advanced materials and coatings. Composite materials, for instance, are gaining traction due to their lighter weight, higher strength-to-weight ratio, and excellent corrosion resistance compared to traditional metals. Ceramic coatings offer superior hardness and wear resistance, extending the lifespan of rolls in abrasive environments. These materials not only improve durability but can also contribute to energy savings by reducing the mass that needs to be rotated or heated.
The concept of "smart rolls" is also becoming a reality. These rolls are equipped with embedded sensors that can monitor various parameters in real-time, such as temperature, vibration, pressure distribution, and even surface wear. This data can be transmitted wirelessly to a central control system, allowing for predictive maintenance, optimized operation, and early detection of potential issues. Imagine a roll that tells you it needs attention before it even shows visible signs of wear! This integration of the Internet of Things (IoT) with industrial paper mill rollers is set to revolutionize maintenance practices and operational efficiency.
Furthermore, sustainability is a growing concern. Future roll designs will likely focus on reducing energy consumption, particularly in the dryer section, where significant heat is used. Innovations in surface technology that improve heat transfer efficiency or reduce sticking can lead to substantial energy savings. Additionally, the focus will be on designing rolls that are easier to recycle or refurbish, minimizing waste and promoting a circular economy within the paper industry. Many experts agree that the move towards more environmentally friendly manufacturing processes will continue to shape the development of these critical components.
It's worth noting that the synergy between roll manufacturers, paper machine builders, and paper mills is crucial for these innovations to take hold. Collaborative research and development will ensure that the next generation of rolls meets the complex demands of a rapidly changing industry, ensuring that paper production remains efficient, high-quality, and sustainable for years to come.
Conclusion: The Enduring Legacy of Rolls in Paper Production
As we've explored, the rolls for paper industry are far more than just cylindrical components; they are the silent, powerful engines driving the entire paper manufacturing process. From the initial formation of the delicate paper web to the final calendering and reeling of the finished product, these precision-engineered components perform an astonishing array of tasks, each critical to the quality and efficiency of production. Their design, manufacturing, and maintenance represent a sophisticated blend of material science, mechanical engineering, and operational expertise.
The journey of paper, from a watery pulp to the smooth sheet you hold, is a testament to the continuous innovation and meticulous care invested in every aspect of paper machine operation, with rolls playing a starring, albeit often unseen, role. As the industry moves forward, driven by demands for higher speeds, better quality, and greater sustainability, the evolution of these industrial paper mill rollers will undoubtedly continue. They will become smarter, more durable, and more efficient, ensuring that the backbone of paper production remains strong and capable of meeting future challenges.
So, the next time you use a paper product, take a moment to appreciate the unsung heroes – the rolls – that worked tirelessly to bring it to you. Their enduring legacy in the world of paper production is undeniable, and their future promises even more remarkable advancements.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website:Rolls for paper industry
About the author: Dr. Alistair Finch is a veteran mechanical engineer with over two decades of experience specializing in industrial machinery, particularly within the pulp and paper sector. His expertise spans the design, manufacturing, and maintenance of critical components like paper machine rolls. Alistair is passionate about optimizing industrial processes through innovative engineering and sustainable practices, making him a recognized authority on the backbone of paper production.