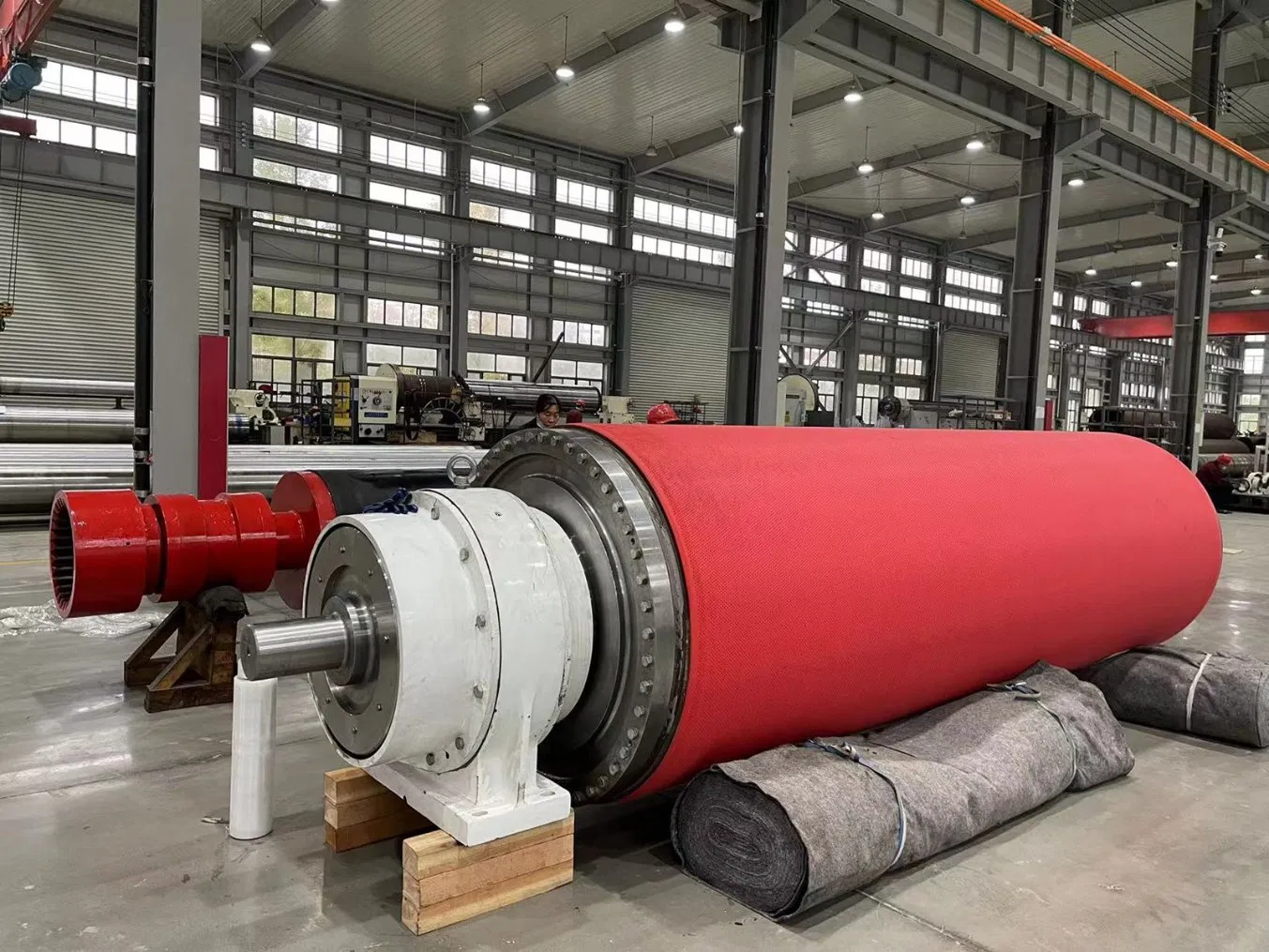
The drying section stands as one of the most energy-intensive and critical stages in the entire papermaking process. At its heart lie the drying section rolls, a series of components working in concert to remove the vast majority of remaining water from the paper web after it leaves the press section. Understanding these rolls – their types, functions, materials, and operational intricacies – is absolutely fundamental for anyone involved in paper production, maintenance, or process optimization. Frankly speaking, without a properly functioning drying section, achieving desired paper properties like strength, smoothness, and dimensional stability becomes impossible. The efficiency of this section directly impacts not only the final product quality but also the overall energy consumption and profitability of the mill. Have you ever stopped to consider the sheer scale of this operation? A typical large paper machine might have dozens, even over a hundred, of these rolls, each playing a vital role in transforming a wet, fragile web into a finished sheet. This article delves deep into the world of drying section rolls, exploring their significance and the engineering marvels they represent.
The Crucial Role of Drying Section Rolls in Water Removal
The primary function of the drying section rolls is straightforward yet immensely challenging: efficient water evaporation. After the press section, the paper web still contains a significant amount of water, typically around 50-60%. The drying section must reduce this moisture content down to the final target, usually between 4-10%, depending on the paper grade. This is achieved primarily through heat transfer. The main players here are the large, steam-heated dryer cylinders (also known as dryer cans). The paper web snakes its way around these heated cylinders, often supported by dryer fabrics or felts, which are guided by separate felt rolls or guide rolls. Heat conducts from the hot cylinder surface through the paper web, causing the water within the sheet to evaporate. Simultaneously, ventilation systems remove the moisture-laden air from the dryer section hood. It's a delicate balance; too much heat too quickly can damage the sheet or cause uneven drying, while insufficient heat leads to low production rates and potential quality issues. The design, arrangement, and surface condition of these rolls are paramount. For instance, the thermal conductivity of the cylinder material, the uniformity of the surface temperature, and the effective contact between the web and the cylinder surface all significantly influence drying efficiency. It's worth noting that the tension control provided by the various rolls is also critical to prevent web breaks and ensure smooth runnability through this long and complex section.
Types of Rolls Found in the Drying Section
The drying section isn't just comprised of one type of roll; it's a carefully orchestrated system involving several distinct roll types, each with a specific purpose. The most prominent are the steam-heated dryer cylinders. These are typically large-diameter, hollow cast iron or steel cylinders heated internally by steam. Their primary job is to provide the thermal energy for evaporation. Then, there are the felt rolls (or fabric rolls/guide rolls). These smaller diameter rolls guide the dryer felts or fabrics, which press the paper web against the heated cylinders, improving heat transfer and supporting the web as it travels between cylinders. Proper alignment and condition of these felt rolls are essential for maintaining felt tension and preventing fabric wear or damage. We also find press rolls within some dryer section configurations, particularly in single-tier or slalom designs, which help ensure intimate contact between the web, the fabric, and the dryer cylinder. Additionally, specialized rolls like spreader rolls might be used to control the width and flatness of the web. The specific configuration – traditional two-tier, single-tier, slalom – dictates the exact arrangement and types of rolls used. Understanding the function of each roll type within a specific machine's configuration is key to effective troubleshooting and optimization. In my experience, overlooking the condition or function of seemingly minor guide rolls can lead to significant operational headaches down the line.
Steam Heated Dryer Cylinders: The Workhorses
Let's focus more closely on the steam-heated dryer cylinders, as they are truly the engines of the drying process. Traditionally made from cast iron due to its good thermal properties and machinability, modern machines may also utilize steel, especially for higher pressure and temperature applications. The internal design is crucial for efficient steam distribution and condensate removal. Systems like siphon pipes (stationary or rotating) are employed to continuously remove the condensed steam (condensate) from inside the cylinder. Why is this so critical? If condensate builds up inside the cylinder, it forms an insulating layer, significantly reducing the rate of heat transfer to the cylinder shell and, consequently, to the paper web. This phenomenon, known as "rimming," can lead to uneven drying and increased energy consumption. Effective condensate removal ensures a uniform surface temperature and maximizes heat transfer efficiency. The external surface of the dryer cylinder is equally important. It must be smooth, clean, and free from defects to ensure good contact with the paper web and prevent marking. Over time, surfaces can become contaminated or corroded, necessitating regrinding or specialized surface treatments to restore optimal performance. Many experts agree that maintaining the integrity of both the internal condensate system and the external drying surface is paramount for peak drying performance.
Felt Rolls and Their Supporting Role
While the steam cylinders provide the heat, the felt rolls (or fabric guide rolls) play an indispensable supporting, yet critical, role. Their primary functions are to guide the dryer fabric accurately, maintain appropriate fabric tension, and ensure the fabric correctly presses the paper web against the dryer cylinders. Think about the path the fabric takes – weaving over and under numerous rolls across the entire length of the drying section. Precise alignment of these felt rolls is non-negotiable. Misalignment can cause fabric tracking issues, leading to uneven tension profiles, premature fabric wear, sheet handling problems, and even catastrophic fabric damage. Felt rolls need to be robust, dimensionally stable, and often feature specific surface characteristics depending on their position and function. For instance, some rolls might be crowned to help center the fabric, while others need to be perfectly cylindrical. Bearing condition is another critical factor; failed bearings can lead to roll seizure, fabric damage, and unscheduled downtime. Regular inspection and maintenance of felt rolls, including bearing lubrication and alignment checks, are vital preventative measures. It's easy to focus solely on the large dryer cans, but to be honest, neglecting the seemingly simpler felt rolls can bring the entire drying section to a standstill just as effectively.
Material Selection and Surface Properties
The choice of materials for drying section rolls is dictated by the demanding operating environment – high temperatures, mechanical stresses, potential for corrosion, and the need for specific thermal properties. As mentioned, cast iron has been a long-standing choice for dryer cylinders due to its heat transfer capabilities, structural integrity, and cost-effectiveness. However, steel is increasingly used, particularly in high-speed machines or those operating with higher steam pressures, offering greater strength. For felt rolls, steel is common, often with specific surface treatments to enhance durability or grip. The surface properties of the rolls, especially the main dryer cylinders, are critical. A smooth, uniform surface ensures maximum contact area with the paper web, promoting efficient heat transfer. Roughness, pitting, or contamination buildup can significantly hinder this process. Consequently, various surface technologies are employed. These can range from simple grinding and polishing to more advanced coatings or treatments designed to improve heat transfer, enhance release properties (preventing fiber picking), increase wear resistance, or provide corrosion protection. For example, metallized coatings (like Tungsten Carbide) can dramatically extend the life of a dryer surface and maintain its smoothness. Selecting the right material and surface treatment involves balancing cost, performance requirements, and the specific challenges posed by the paper grade being produced.
Operational Challenges and Maintenance Strategies
Operating a paper machine drying section efficiently presents numerous challenges. Maintaining uniform cross-machine moisture profiles is a constant battle, influenced by factors like uneven stock distribution, press section performance, and variations in dryer cylinder surface temperatures. Condensate removal issues, as discussed earlier, are a frequent culprit behind uneven drying and energy waste. Bearing failures, whether on dryer cylinders or felt rolls, represent a significant cause of unscheduled downtime and can be costly to repair, especially on the main dryer cans. Roll surface contamination or damage can lead to paper quality defects (like picking or marking) and reduced heat transfer. Dryer fabric performance is also intertwined with roll condition; poor roll alignment or surface issues can shorten fabric life considerably. Effective maintenance strategies are therefore crucial. These include:
- Regular inspections of roll surfaces, bearings, and structures.
- Consistent monitoring of steam and condensate systems.
- Periodic roll grinding or resurfacing to maintain optimal surface condition.
- Predictive maintenance techniques, such as vibration analysis and thermal imaging, to detect potential bearing or condensate issues before they cause failure.
- Precise roll alignment checks and corrections.
Energy Efficiency Considerations
The drying section is notorious for being the largest single energy consumer on a paper machine, often accounting for 50-70% of the total steam usage. Therefore, any effort to improve energy efficiency in this section can yield substantial cost savings and environmental benefits. Several factors related to the drying rolls directly impact energy consumption. Ensuring efficient condensate removal is paramount; poor removal leads to higher steam pressure requirements to achieve the same drying rate. Optimizing heat transfer by maintaining clean, smooth dryer surfaces and ensuring good web-to-cylinder contact via proper fabric tension (controlled by felt rolls) reduces the energy needed per ton of paper. Insulating the dryer cylinder heads minimizes heat loss to the surrounding environment. Furthermore, the design of the steam and condensate system itself plays a huge role. Cascading steam systems, where steam flows from higher-pressure sections to lower-pressure sections, can significantly improve thermal efficiency. Proper hood design and ventilation are also critical to efficiently remove evaporated moisture without excessive air heating. Have you considered how optimizing the performance of individual rolls contributes to the overall energy picture? Even seemingly small improvements, when multiplied across dozens of rolls, can make a noticeable difference. Our company focuses on providing high-efficiency components and system analysis services designed to pinpoint and address sources of energy waste within the drying section.
Innovations and Future Trends in Dryer Roll Technology
The technology surrounding drying section rolls is continuously evolving, driven by the demands for higher speeds, better paper quality, improved energy efficiency, and enhanced safety. One significant area of innovation lies in dryer cylinder design and materials. Lighter weight designs, potentially using composite materials or advanced steel alloys, could reduce inertial loads and potentially improve heat transfer characteristics. Advanced internal condensate removal systems, such as high-efficiency siphons and turbulence bars, promise more uniform temperature profiles and better energy efficiency. Surface technology is another active area. Novel coatings are being developed to offer superior combinations of heat transfer, durability, and release properties, potentially tailored to specific paper grades. For felt rolls, advancements focus on improved bearing designs for longer life and reliability, as well as lighter constructions and specialized surfaces for better fabric handling. Furthermore, the integration of advanced sensors and monitoring systems directly onto or within the rolls is a growing trend. These systems can provide real-time data on temperature profiles, vibration, and other critical parameters, enabling more sophisticated process control and predictive maintenance. It's fascinating to see how engineering continues to push the boundaries in optimizing what might seem like a mature technology, constantly seeking incremental gains in performance and efficiency.
The Impact of Drying Rolls on Final Paper Quality
The condition and operation of the drying section rolls have a profound impact on the final quality attributes of the paper. Uneven drying, often caused by inconsistent dryer surface temperatures or poor condensate removal, directly leads to non-uniform moisture profiles in the finished sheet. This can cause issues like curl, cockling, and dimensional instability, making the paper difficult to print on or convert. The surface characteristics of the dryer cylinders themselves can imprint onto the paper web; a rough or damaged cylinder surface can result in poor sheet smoothness or surface defects. Conversely, a well-maintained, smooth dryer surface contributes positively to the final gloss and smoothness of coated and uncoated grades. Fiber picking, where fibers adhere to the dryer surface, is another quality issue linked to roll condition and surface properties, often exacerbated by incorrect temperatures or inadequate surface release characteristics. Furthermore, the tension control exerted by the system of rolls throughout the drying section influences the sheet's strength properties, particularly its stretch and tensile strength development during drying under restraint. Frankly speaking, achieving consistent, high-quality paper requires meticulous attention to the state and operation of every roll in the drying section, ensuring they work together harmoniously to dry the sheet uniformly and gently.
Optimizing Performance: Our Solutions
Understanding the complexities of drying section rolls is the first step; optimizing their performance for maximum efficiency, reliability, and paper quality is the next. This often involves addressing common issues like inefficient condensate removal, uneven temperature profiles, surface wear or contamination, and bearing reliability problems. Our company specializes in providing advanced solutions tailored to enhance drying section performance. We offer high-performance dryer cylinders engineered for optimal heat transfer and condensate removal, potentially incorporating advanced materials or internal designs. We also provide state-of-the-art surface coatings and treatments designed to improve durability, enhance heat transfer, and provide excellent release properties, minimizing issues like picking and extending the time between maintenance shutdowns. For felt runs, we supply robust, precision-engineered felt rolls and advanced bearing solutions designed for longevity in harsh operating conditions. Beyond components, our expertise extends to system analysis and optimization services. We can assess your existing drying section, identify bottlenecks or inefficiencies using diagnostic tools like thermal imaging and steam system audits, and recommend targeted upgrades or process adjustments. Whether it's improving energy efficiency, boosting production rates, or enhancing final paper quality, our products and services are designed to help paper mills get the most out of their critical drying section assets. Why struggle with persistent drying issues when expert solutions are available?
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Dryer Section Rolls
In conclusion, the rolls within the paper machine drying section – from the massive steam-heated cylinders to the numerous felt guide rolls – are far more than simple rotating components. They represent a sophisticated system engineered to perform the critical and energy-intensive task of water removal, fundamentally shaping the properties of the final paper product. Understanding the drying section rolls, their specific functions, material science, operational challenges, and maintenance requirements, is essential for efficient papermaking. The interplay between heat transfer, condensate removal, web handling, and surface interaction dictates not only the drying rate and energy consumption but also crucial quality parameters like moisture profile, smoothness, and strength. As technology advances, innovations in roll design, materials, surface treatments, and monitoring systems continue to offer opportunities for improvement. Whether focusing on maximizing throughput, minimizing energy costs, or achieving superior paper quality, a deep appreciation for the role and optimization of these rolls remains central to successful paper production. Their performance is, quite literally, foundational to the finished sheet.
For more detailed information, please visit our official website: Drying Section Rolls